Do you use .NET Aspire to simplify cloud-native development?
Last updated by Eddie Kranz [SSW] 11 months ago.See historyBuilding cloud-native applications can be challenging due to their complexity and the need for scalability, resilience, and manageability.
There are lots of ways to build cloud-native applications and the overwhelming number of choices can make it difficult to know where to start.
Also, the complexity of modern cloud-native applications can make them difficult to manage and maintain.
.NET Aspire is a powerful set of tools, templates, and integrations designed to streamline cloud-native app development with .NET. It offers a consistent approach to orchestration, standardized integrations, and developer-friendly tooling to help you build robust, production-ready applications.
Video: Cloud Native Aspirations with .NET Aspire | Matt Wicks & Rob Pearson | SSW User Groups (1h 28 min)
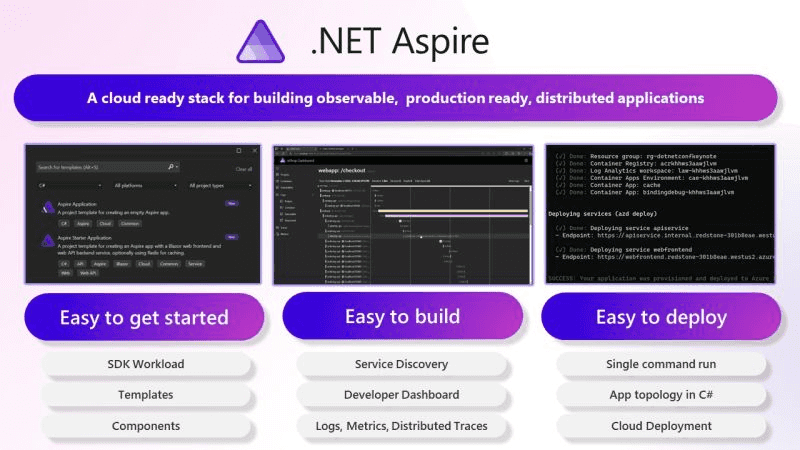
.NET Aspire addresses common pain points in cloud-native development:
Orchestration
.NET Aspire helps you manage interconnected services and resources in your application by:
- Automatically setting up service discovery and environment variables
- Providing tools to spin up local containers and configure dependencies
- Simplifying complex setups with clear abstractions, reducing the need for low-level configuration
Integrations
.NET Aspire integrations make it easy to connect to essential services:
- NuGet packages like
AddRedisorAddAzureServiceBusClientstreamline configuration and health checks - Standardized interfaces reduce boilerplate code and ensure seamless connectivity
Tooling and Templates
Leverage predefined templates and tooling to:
- Generate projects with common configurations like health checks and telemetry
- Save time with opinionated defaults for service discovery, logging, and monitoring
- Kickstart new projects or integrate Aspire into existing .NET apps
Example - Adding Redis Cache to a .NET Core app
The old way - with Docker Compose
- Manually set up a Redis container (e.g., using Docker Compose).
version: '3.9'
services:
redis:
image: redis:latest
container_name: redis-cache
ports:
- "6379:6379"
environment:
REDIS_PASSWORD: examplepassword # Optional, for enabling authentication
command: ["redis-server", "--requirepass", "examplepassword"] # Optional, for setting up a password
volumes:
- redis_data:/data # Persist data locally
volumes:
redis_data:
driver: local- Write custom code to handle connection strings and inject them into your application (this needs to be manually kept in sync with all your environments)
var redisConnection = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("REDIS_CONNECTION_STRING") ?? "localhost:6379";
services.AddStackExchangeRedisCache(options =>
{
options.Configuration = redisConnection;
options.InstanceName = "SampleInstance";
});Figure: Bad Example - Manually setting up Redis cache 🥱
The new way - with .NET Aspire
Aspire handles Redis setup and connection string injection for you:
- Configure your Aspire application and pass a reference to Redis Cache
var builder = DistributedApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
var cache = builder.AddRedis("cache");
builder.AddProject<Projects.MyApp>("app")
.WithReference(cache)
.WaitFor(cache);- Add the client integration for Redis
public static class DependencyInjection
{
public static void AddInfrastructure(this IHostApplicationBuilder builder)
{
builder.AddRedisClient("my-redis-connection-string");
}
}Figure: Good Example - Simple Redis setup with .NET Aspire 🚀
No need to write Docker Compose files. No need for yaml 🤮. Connection string is automatically injected.
Get started with Aspire
You can test out Aspire by running the SSW.CleanArchitecture template - Let us know what you think!

