Do you know the best way to prevent secrets leaking from your code repository?
Last updated by Matt Wicks over 3 years ago.See historyDespite tooling coming a long way to prevent it, accidentally committing a config file with some secrets in it is far too easy to do.
Up to 2022, GitHub had detected more than 700,000 secrets across thousands of private repositories using secret scanning for GitHub Advanced Security:
Video: Github Secrets Leak Prevention (3 min)Once this occurs, amongst other things, you need to:
- assume breach
- rotate secrets
- update affected applications
- notify affected parties
This is a lot of stressful work!
On GitHub, what actions do we need to take to make it better?
GitHub Secret Scanning is a freemium feature for public repositories (not configurable). Otherwise, you need to be a GitHub Enterprise Cloud customer with Advanced Security to utilize it.
How does GitHub know it has found a secret?
Partners can automatically register their secret patterns and get notified automatically when GitHub detect secret with that pattern in a repo. Once notified, the partner can invalidate the secret. For example, if GitHub found a Octopus Deploy API Key in a repo; it would call a webhook to tell Octopus to invalidate it. There is a long list of supported partners at GitHub - Secret Scanning Partners
Setting up on a public repo (free)
Nothing to configure! GitHub will always send alerts to partners for detected secrets in public repositories.
Setting up on GitHub Enterprise (with Advanced Security)
Follow the steps on GitHub - Configuring secret scanning for your repositories.
As a bonus, you can shift this left a bit and block developers from pushing code to the repo if GitHub finds a secret in the push. This has the benefit of not requiring secret rotation (as no one else was able to pull the branch). See GitHub - Protecting pushes with secret scanning.
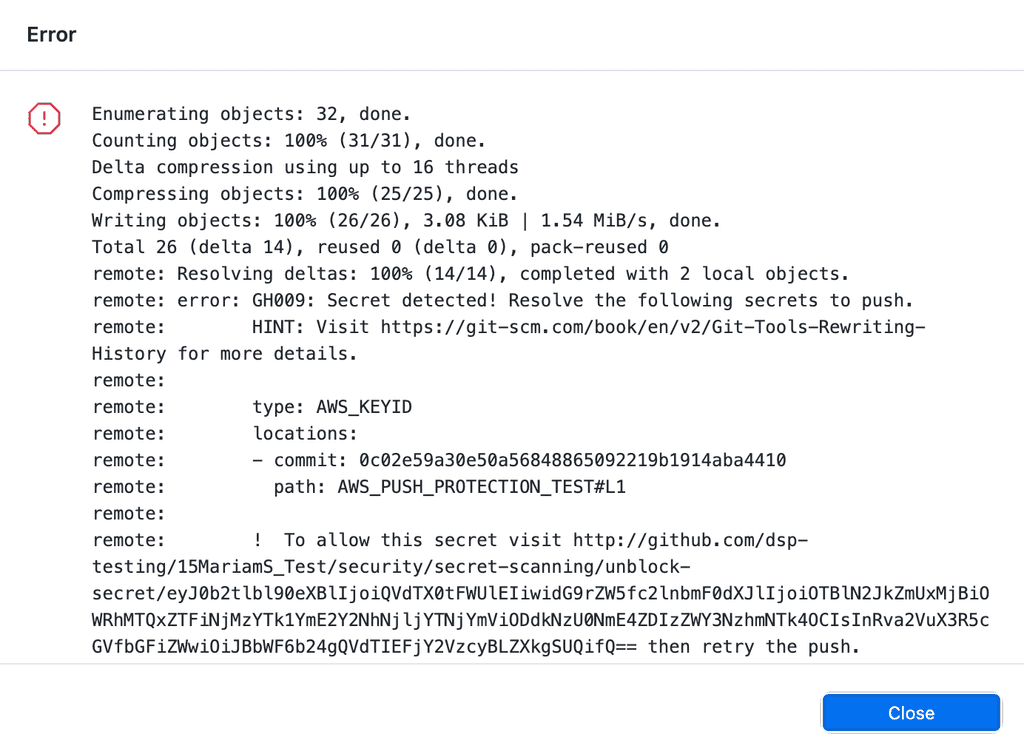
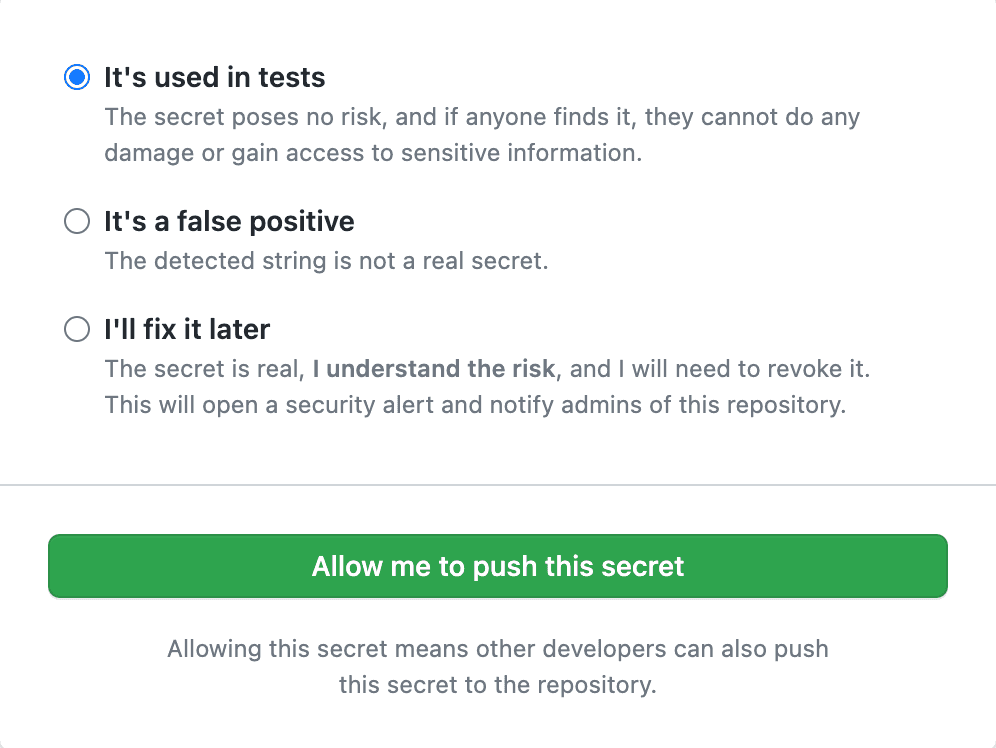
If you have secrets patterns that aren't natively supported - you can use regexes to define these custom patterns for GitHub to look out for. See GitHub - Define custom patterns
