Rules to Better Reporting Services - 61 Rules
SQL Server Reporting Services is a comprehensive, server-based reporting solution that can author, manage, and deliver both paper-oriented and interactive, Web-based reports. Do you agree with all these rules? Are we missing some? Let us know what you think.
🔊 Historical (2006) Listen to Adam's podcast on these rules with Greg Low (42 min)
⚠️ While SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) is still in use, it is considered legacy technology. For modern data reporting and analytics, Power BI is the recommended solution. Check out our Rules to better Power BI.
If you need consulting help, visit Enterprise Reporting and BI and book in a consultant.
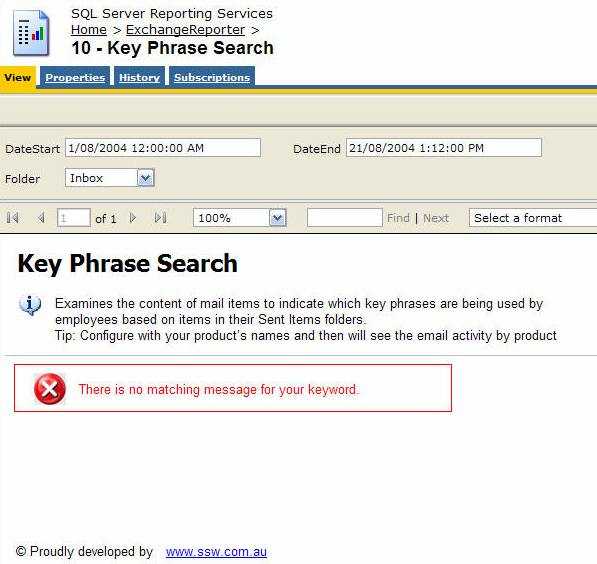
By default SSRS will track reporting execution for the last 60 days. This might be OK in most cases, but you may want to adjust the retention days if you want better report usage statistics.
To update the value you can:
- Connect to the ReportServer database in SQL Management Studio
- Execute the following script and update the value to the number of days you want to track
EXEC SetConfigurationInfo @Name=N'ExecutionLogDaysKept',@Value=N'365'After you have this, you can query the ExecutionLog table to find useful information about report execution like:
- Which users are actively using the reports
- How long reports are executing
- The last time a report was executed
SSRS keeps track of each report that gets executed and records useful information like:
- How long did the report take to generate
- Who requested the report
- When was the report generated
- Report Parameters used
So it's quite simply a matter of querying the ReportServer database for information in the ExecutionLog table.
WITH RankedReports AS (SELECT ReportID, TimeStart, UserName, RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY ReportID ORDER BY TimeStart DESC) AS iRank FROM dbo.ExecutionLog t1 JOIN dbo.Catalog t2 ON t1.ReportID = t2.ItemID ) SELECT t2.Name AS ReportName, MAX(t1.TimeStart) LastAccessed, --t1.UserName, t2.Path, SUBSTRING(t2.Path, 0, CHARINDEX('/', t2.Path, 2)) ParentFolder, t1.ReportID FROM RankedReports t1 JOIN dbo.Catalog t2 ON t1.ReportID = t2.ItemID WHERE t1.iRank = 1 GROUP BY t2.Name, Path, ReportID ORDER BY MAX(t1.TimeStart) DESC;The query above gives you the last reports that were accessed (Credit to Eric Phan - SSRS - Find out which reports are being used (handy for migrating only the useful reports to a new server))
Like any solution, Reporting Services has its pros and cons. From our experience, we have discovered these things about Reporting Services:
Cons
- Parameters - you are forced to use built-in controls.
- Query string - when you change the parameters and refresh a report, the values do not appear directly in the query string, making it hard to copy/paste URLs.
- Can't separate SQL into a strongly-typed dataset or middle-tier object like in ASP.NET.
- There are potential difficulties with the deployment of RS reports and the exposing of them. However, once we have the infrastructure...
- Not able to work natively with modern .NET.
Pros
- You can develop read only reports faster in Reporting Services than ASP.NET.
- Maintenance with RS is easier than ASP.NET, as with most cases you don't have to write any code.
- Flexibility with groupings and totals is easier. In ASP.NET you would need to iterate through the DataSet, keeping variables with the totals.
- Parameters are built-in. In ASP.NET there is code.
- Drilldown interactivity. In ASP.NET you need to code up a treeview.
- Users can have reports automatically emailed to them on a schedule.
- Users can export natively to PDF and XLS, plus a variety of other popular formats.
Nowadays, better technologies are used to handle reports. Examples include
- Power BI: cloud-based solution that provides visually appealing reports and dashboards.
- HTML based reports: HTML frameworks have evolved significantly, making it quick and easy to make great reports.
For a more detailed comparison between reporting solutions, take a look at our Guidelines for Report Solutions - Web Clients.

Figure: Reporting Services has built-in support for PDF/XLS export and can be embedded in your ASP.NET pages Figure: How to migrate SSRS reports from an old server to another
Let's say you want to migrate SSRS reports from an old reporting service server (e.g. SQL Server 2008 R2) to a new one (e.g. SQL Server 2016). What involves?
There are 3 steps:
Step 1: Find the reports that don't need to be migrated
- Find those reports are not-in-use, as per a rule: Do you know which reports are being used?
-
Find creators of those reports, by clicking “Detail Views” in reports folder
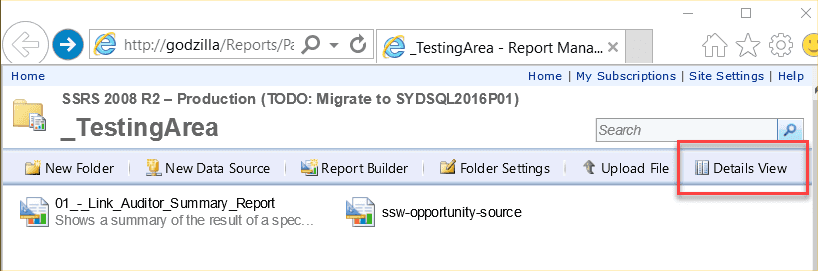
Figure: Find reports creators by clicking "Details View" inside report folder -
Send an email to report creater ask for permission to delete
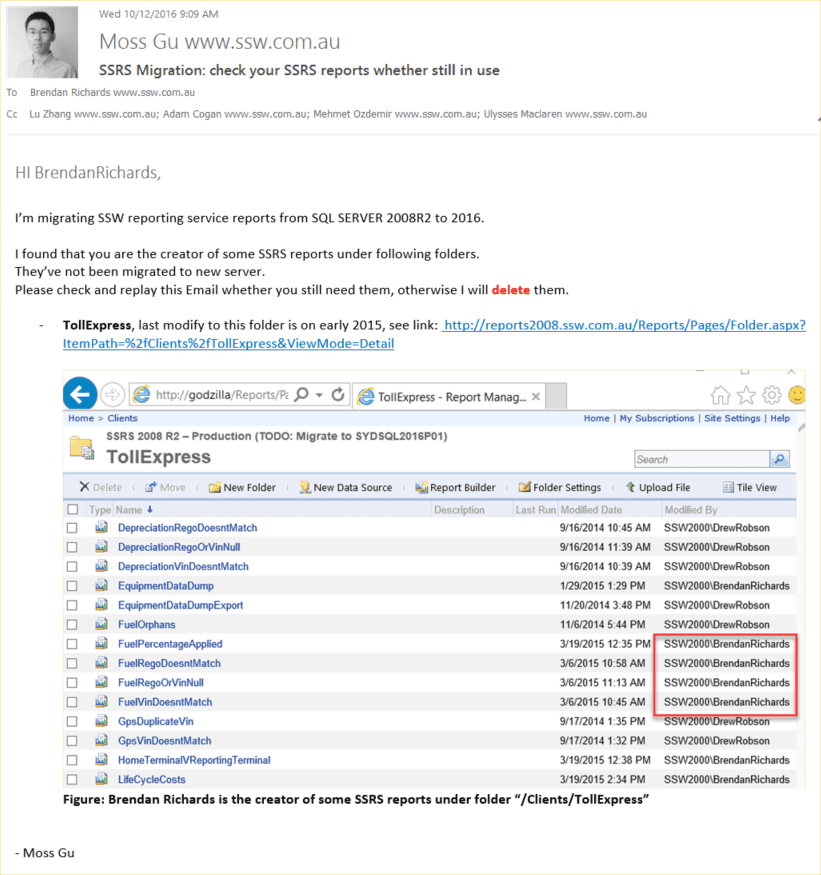
Figure: Send an email to ask permission 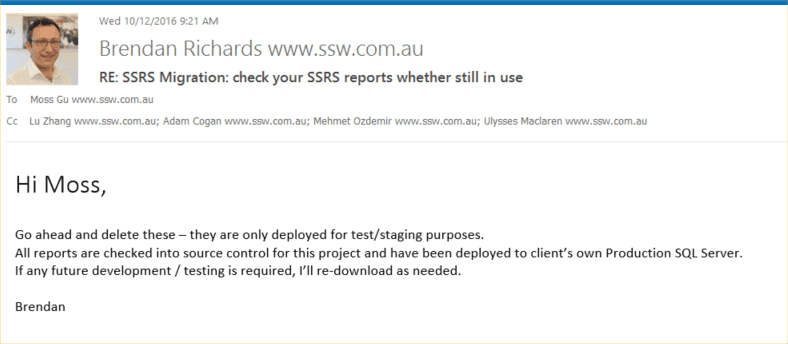
Figure: Email received with permission to delete from creator
2. Migrate those in-use reports from old server to new server
Tip: Use the ReportSync tool to save time.
3. Check audit results
- Run SSW SQL Reporting Service Auditor on both sides
- Compare audit results. Note that even error and warning messages also need to be the same
If audit results are exactly the same on old and new servers, it indicates that migration is successful.
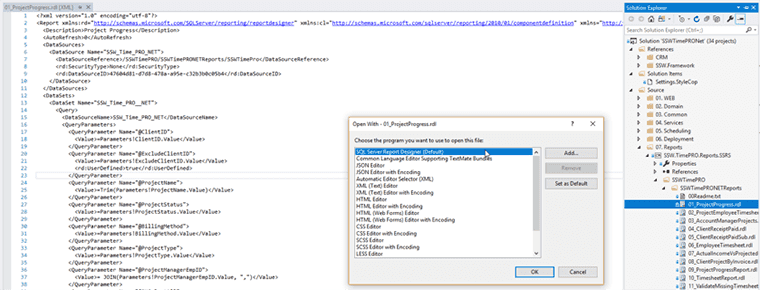
When working with SSRS reports, you need to have the right type of project otherwise it will be difficult for a developer, to create new reports or update existing ones.
If you have some reports and want to check them into source control, if you add them to project that is not a report project, your reports will not open in the design/preview view (allowing to see the DataSource and DataSets). They will open in the XML view (which is not pretty to work with).
To open the reports in the right view you will need to:
- Be sure that you VS has the tool/extensions Microsoft Reporting Services Projects installed, go to Tools | Extensions and Updates | Online, and search for services
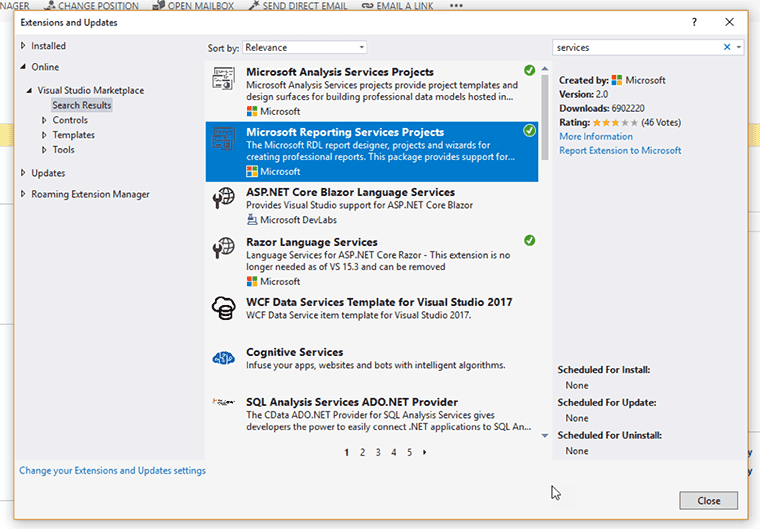
Figure: Checking Microsoft Reporting Services Projects is installed - In SQL Server Data Tools (SSDT) for Visual Studio website you will find all the instructions to install the tool via Marketplace or SSDT standalone installer.
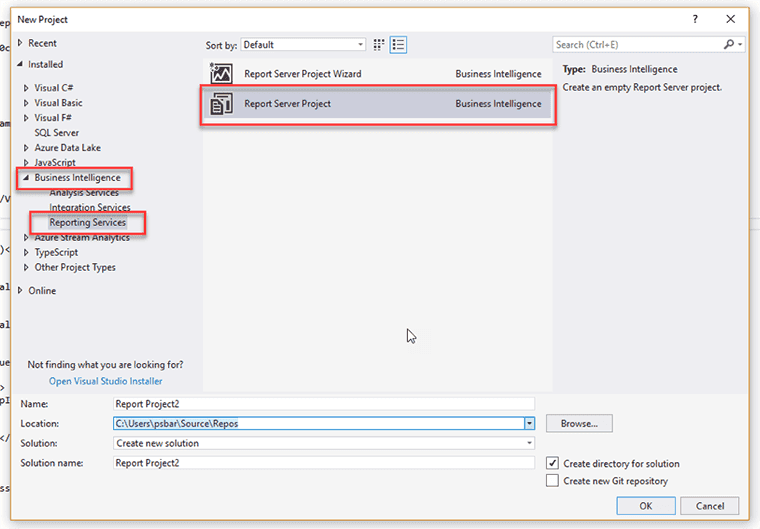
- Create the project selecting Business Intelligence | Reporting Services | Report Server Project
- Add existing reports and create your new DataSource (based in the information on your Report Portal)
The default configuration for Report Server isn't accessible by most mobile browsers and some desktop browsers too. You can adjust the authentication types allowed to increase the range.
The configuration file for the Report Server is named RSReportServer.config and the default location is:
C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSRS13.MSSQLSERVER\Reporting Services\ReportServer
You should make a backup of the configuration before editing it so you can rollback if you make a mistake.
We normally change the AuthenticationTypes node from:
<AuthenticationTypes> <RSWindowsNegotiate /> </AuthenticationTypes>to:
<AuthenticationTypes> <RSWindowsNegotiate /> <RSWindowsKerberos /> <RSWindowsNTLM /> </AuthenticationTypes>Check out the different Authentication Types in the Report Server documentation and select the types that suit your needs.
More details on configuring Windows authentication on the report server can be found here: Configure Windows Authentication on the Report Server.
Here are the steps to subscribe a report:
- Open IE, go to the folder view which contains the report you're going to subscribe.
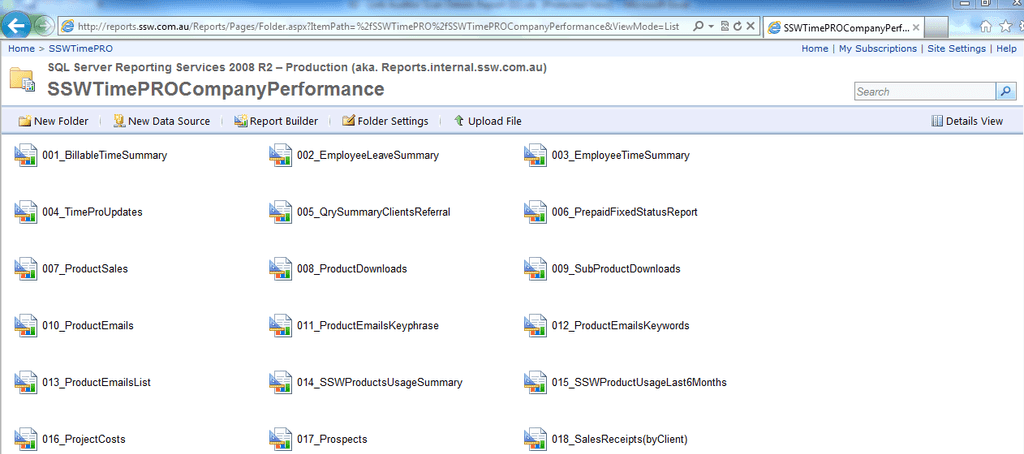
Figure: Reports folder view - Click the report you're going to subscribe and select "Subscribe...".

Figure: Subscribe report - Configuring the subscriber's email address, report render type and schedule.
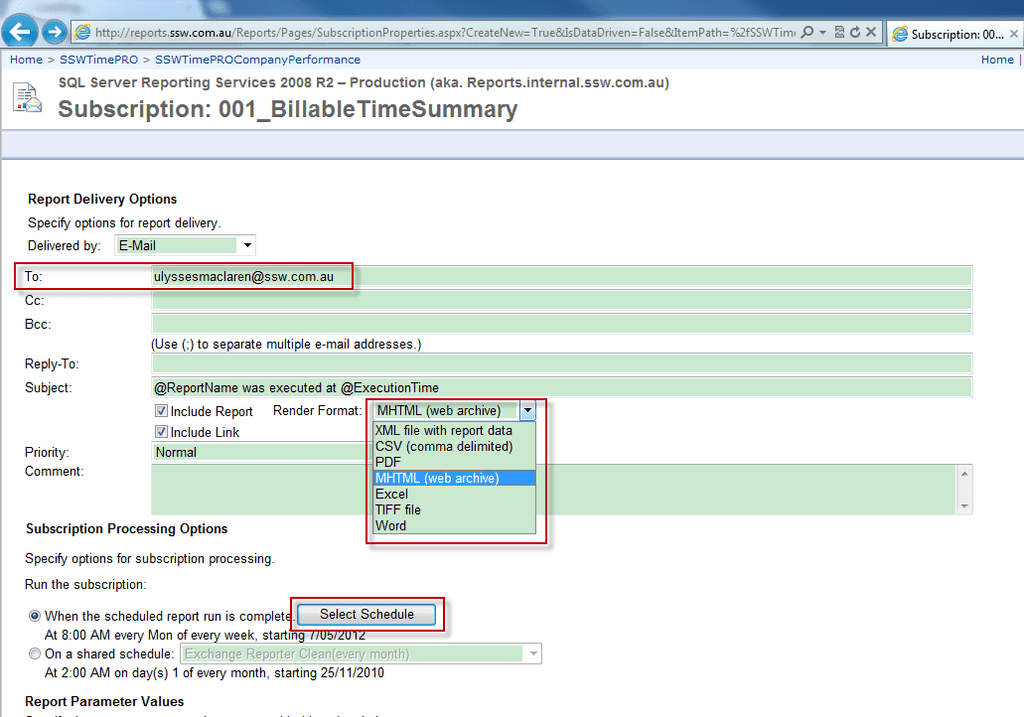
Figure: Configuring subscribe settings SQL Server 2008 R2 Reporting Services comes with some great samples that will help get you started. Unfortunately, they aren't installed by default.
These samples include:
- Report Project based on the Adventure Works 2008 R2 database
- Report Builder Model based on the Adventure Works 2008 R2 database
Upon installing the samples successfully, you should see 3 folders (shown below) in your Report Manager.

Figure: A proper installation of the samples For more information, visit the following links:
A lot of the time, you will want a hard copy of your reports. Obviously reports are different sizes on screen and on paper, so you need to format your report so it exports to PDF and prints properly. Here's how.
- Change the report's page width to 28cm (or 11in) and top and bottom margins to 0.5cm.
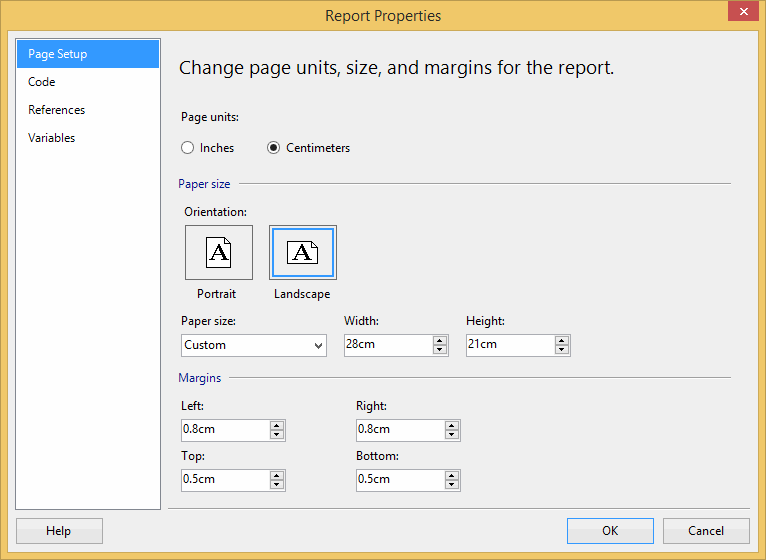
Figure: Good example - For proper printing, first change the Report's Page Width to 28cm (or 11in) and top and bottom margins to 0.5cm - Change the Body width to 25.4cm (or 10in)
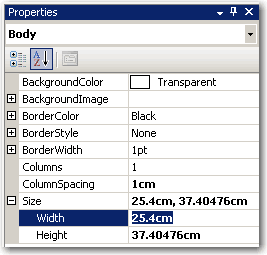
Figure: Good example - Then change the Report's Body Width to 25.4cm (or 10in) You can see the 0.5cm margin looks much better than 1cm, and you have more space to organize your content, especailly for a landscape print view.
- Resize report items (tables and charts) to fit the page. The easiest way to do this is to select (Ctrl+click) all report items that should span the whole width of the page, and set their Width property to 25.4cm (or 10in).
Tip: Export your report to PDF and do a print preview, so you don't have to print a lot of testing pages to find out the best page settings.
Tip: Remove top and bottom paddings in header and footer text can also give you more space.
Note: Reporting Services reports accept both inches and cm, so you can use either.
We have a program called SSW Code Auditor to check for this rule.
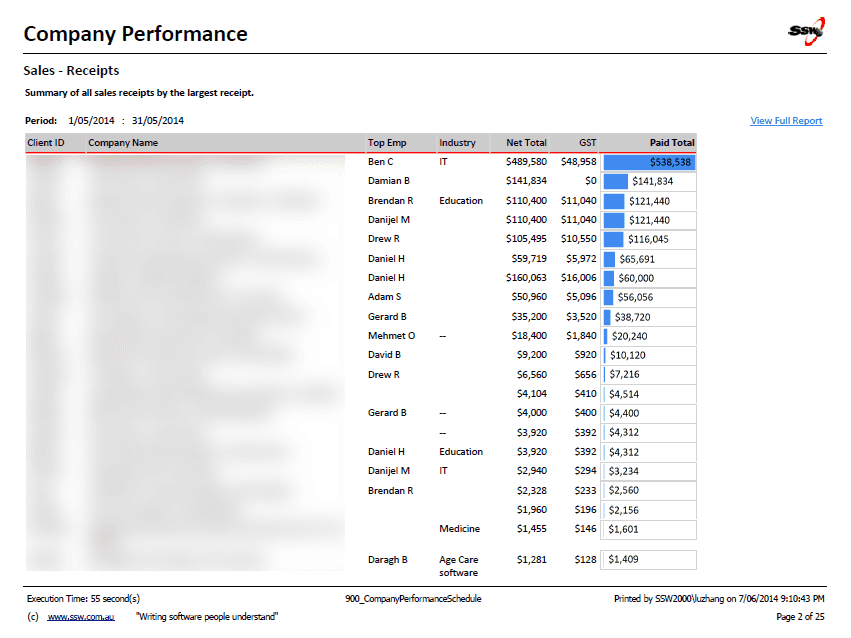
When designing custom applications you want to include branding on reports. You should always include a useful and informative footer at the bottom of your reports.
Include:
- Date and Time Printed and User who printed it - see warning below (e.g. Printed by SSW\DaveSmith on 3/1/2024 3:16:30 PM)
- Execution Time (e.g. Execution time: 1 minute, 10 seconds)
- Page x of y (e.g. Page 3 of 10)
- Link to company website + slogan (e.g.
www.ssw.com.au- Enterprise Sopftware Development)
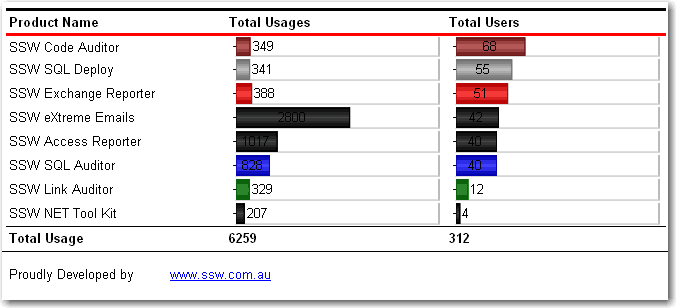
Bad example - This footer doesn't provide any useful information 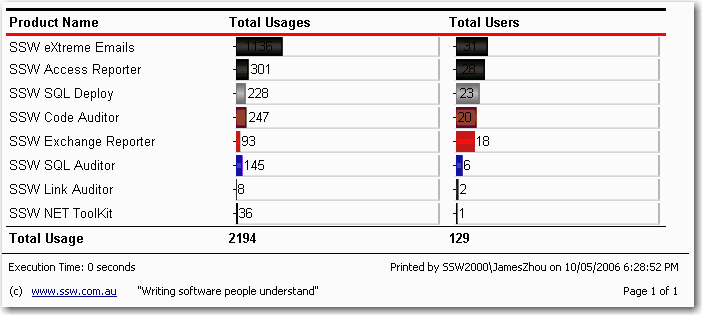
Good example - Useful and informative information should be displayed in your report footer Use these handy report expressions to show the above information.
Note: Do not use
System.DateTime.Nowfor Execution Time because if you do it will return the result at time of printing the document/PDF. Instead store the value in a variable (for exampleGroupExecutionTime) and then call that.Use these handy report expressions to show the above information.
Footer Item Expression Sample Output Date and Time printed / User ID ="Printed by " + User!UserID + " on " + Globals!ExecutionTime.ToString() Printed by SSW2000\JatinValabjee on 3/1/2006 3:16:30 PM Execution Time ="Execution Time: " + IIf(System.DateTime.Now.Subtract(Globals!ExecutionTime).TotalSeconds < 1, "0 seconds", ( IIf(System.DateTime.Now.Subtract(Globals!ExecutionTime).Hours > 0, System.DateTime.Now.Subtract(Globals!ExecutionTime).Hours & " hour(s), ", "") + IIf(System.DateTime.Now.Subtract(Globals!ExecutionTime).Minutes > 0, System.DateTime.Now.Subtract(Globals!ExecutionTime).Minutes & " minute(s), ", "") + IIf(System.DateTime.Now.Subtract(Globals!ExecutionTime).Seconds > 0, System.DateTime.Now.Subtract(Globals!ExecutionTime).Seconds & " second(s)", "")) ) Execution time: 1 minute, 10 seconds Page x of y ="Page " + Globals!PageNumber.ToString() + " of " + Globals!TotalPages.ToString() Page 3 of 10 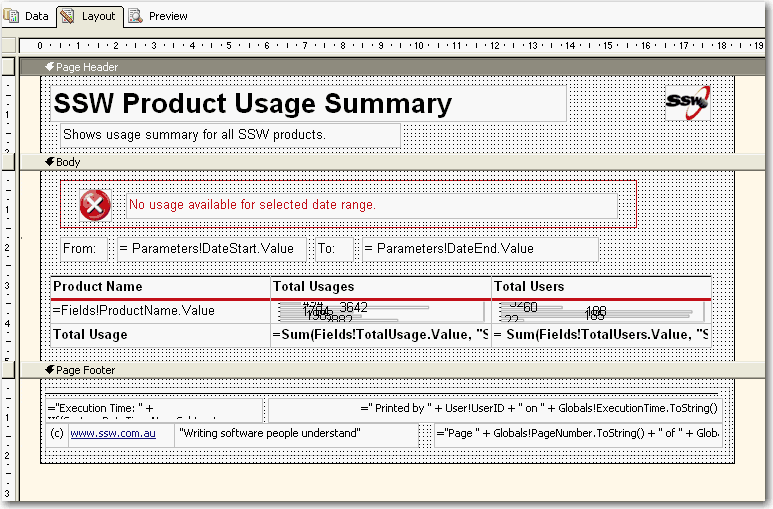
Figure: Good example - Footer in visual studio designer Tip: Copy and Paste this XML into the <PageFooter> for the recommended footer of all your *.rdl files.
<PageFooter> Paste here </PageFooter>Warning: Adding the User who printed it stops all data-driven subscriptions.
When you try to add the User your data-driven subscriptions will fail with the following error:
'The '/GroupHealth' report has user profile dependencies and cannot be run unattended. (rsHasUserProfileDependencies)'.
A quick workaround is to add a user function to fallback the error to a nice message, like "SYSTEM":
Public Function UserName() Try Return Report.User!UserID Catch Return "System" End Try End FunctionUse above function to replace your reference to
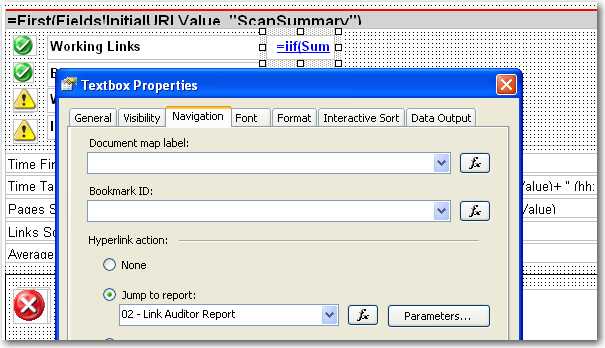
Report.User!UserIDwill allow the subscription to work correctly.The Hyperlink Action allows users to navigate between reports smoothly, but users may ignore the navigation functionality in your reports.
With the underline effect on your hyperlink items, it will be easy for users to find the navigation on your reports.
We have a program called SSW Code Auditor to check for this rule.
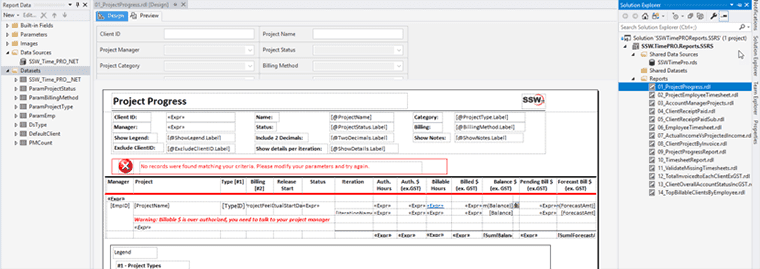
Errors on reports should not occur but when they do it is best to make it clear to the reader that they have just experienced an error.
How evident are the error messages on the 1st report below?
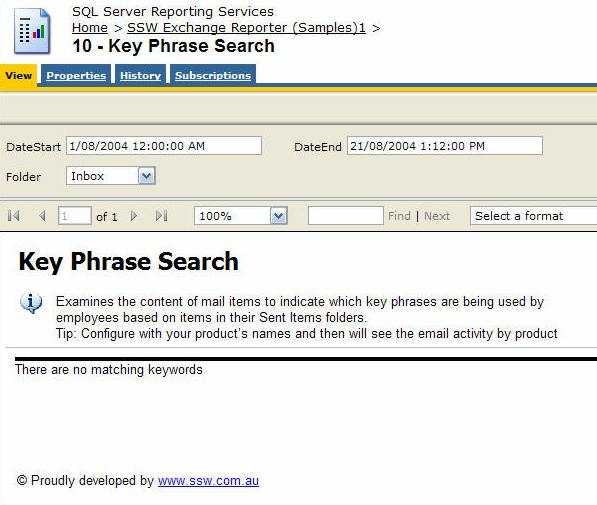
Figure: Bad example - Using the default NoRows property of the table control - error message is not clear enough Reporting Services allows you to set the 'NoRows' property of a table control to warn your user when there is no data available. This is similar to handle the 'NoData event' in Access report but there is no advanced control on this message, not even a Color property - this has not been improved in RS2005, see our Better Software Suggestions page.
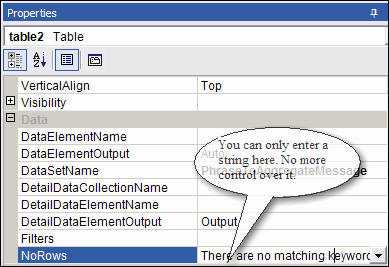
Figure: NoRow property of Table control only allow simple string Here's how to add a custom "NoData" textbox with a red icon to your report:
- Add a rectangle to the top of your report, above any report items in the body. Set its BorderColor to Red.
- Drop a textbox into the rectangle and give it the value No records were found matching your criteria. Please modify your parameters and try again.
- Add an Image control to it. This opens in a New Window as the Image (add an error icon ❌ to your Images folder in your solution and reference it like Images/fatalerrorinfo.gif). Your report will now look similar to the one below.
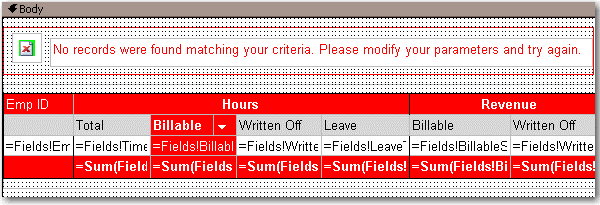
Figure: Adding a custom error message to your report - In the Hidden property of the Rectangle, add an expression to show/hide it depending on whether any rows were returned. Use the following expression, substituting the bold for your own values (e.g. checking if the sum of all orders is < 0)
--Expression to set the visibility of the error message controls = iif( Sum(Fields!SaleTotal.Value, "MyDataSet")>0, True, False)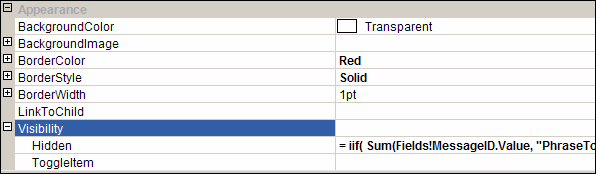
Figure: The Hidden property of the rectangle - Group all other report items into a rectangle - you want to be able to show and hide them dynamically.
- In the Hidden property of this Rectangle, add an expression to show/hide it depending on whether any rows were returned. Switch the True and False values around, so that it shows if it does have records, and hides if it does not have records (the opposite behaviour to the error box). So, in the example above, the expression would be:
--Expression to set the visibility of the main report items = iif( Sum(Fields!SaleTotal.Value, "MyDataSet")>0, **False**, **True**)A professional report should have consistent name.
Figure: Bad example - Inconsistent report name 
Figure: Good example - Consistent report name A professional report should have the feedback information, then users can give suggestions directly to the designers.

Figure: Good example - Include feedback information See how AI is used in Power BI to provide feedback in Reports in this rule
Things in a report page header repeat on every page. To avoid duplicate and save paper when printing, we put content as less as possible in the header.
Figure: Bad example - 4 lines in the page header 
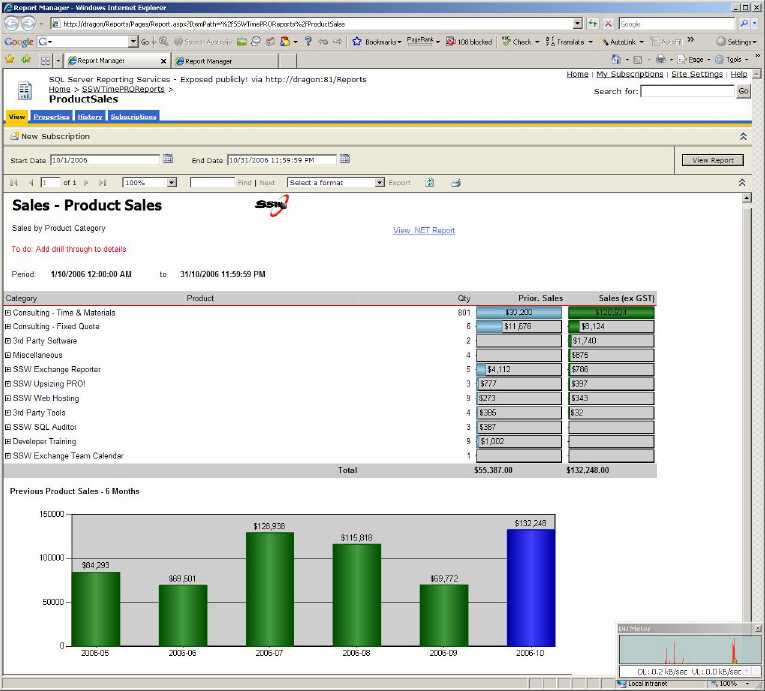
Figure: Good example - One line in the page header When you are working with reports that use time-based data (sales figures, employee productivity etc.), it is handy to see how you went this month compared to the past 6 months. The best way to show this is on a bar chart.
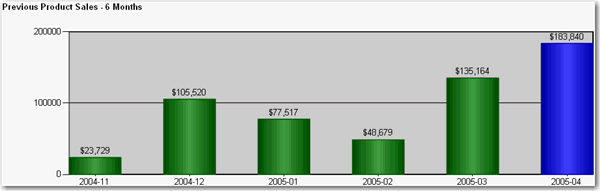
Figure: Good example - Use of bar chart to show the past 6 months of totals at the end of your report for easy comparison To do this:
- Create a new dataset in your report.
- Enter the following query, substituting "MyDate" for the name of the date field you are referencing, "MyTable" for the view or table you are selecting from, and "@pEndDate" for the name of the report parameter you are using for the data end date:
SELECT DISTINCT TOP 6 CONVERT(varchar(12), Year(MyDate), 101) + '-' + RIGHT('0' + Convert(Varchar(2), MyDate, 101), 2) AS Y , Sum(PaidTotal) * -1 AS Total FROM MyTable WHERE MyDate BETWEEN DateAdd(Month,-5,convert(varchar(12), Month(@pEndDate)) + '/1/' + convert(varchar(12), Year(@pEndDate))) AND CASE WHEN datepart(d,@pEndDate) = 1 THEN DateAdd(d, 1, @pEndDate) ELSE @pEndDate END GROUP BY CONVERT(varchar(12), Year(MyDate), 101) + '-' + RIGHT('0' + Convert(Varchar(2), MyDate, 101), 2) ORDER BY CONVERT(varchar(12), Year(MyDate), 101) + '-' + RIGHT('0' + Convert(Varchar(2), MyDate, 101), 2)- Configure the new added parameter 'pEndDate'
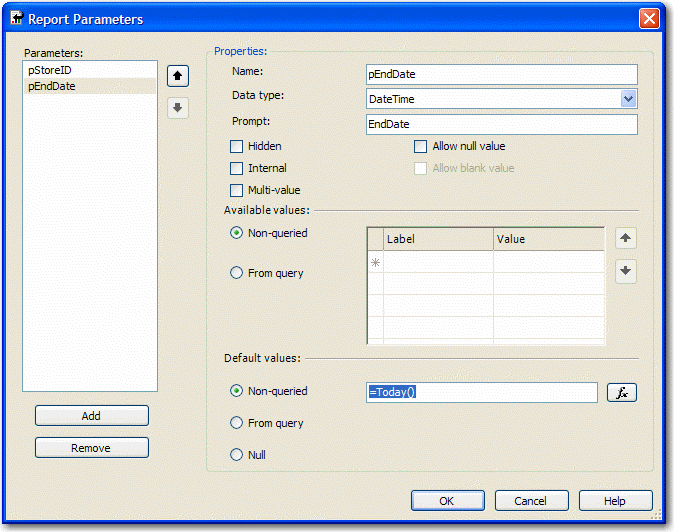
Figure: Change Data Type to DateTime and assign to the proper default values - Add a chart to your report in Layout view and change its type to "Simple Column".
- Drag the "Total" field from the Datasets window into the Data area on the chart, and the "Y" field into the Category area. Your chart will now look similar to the one below.
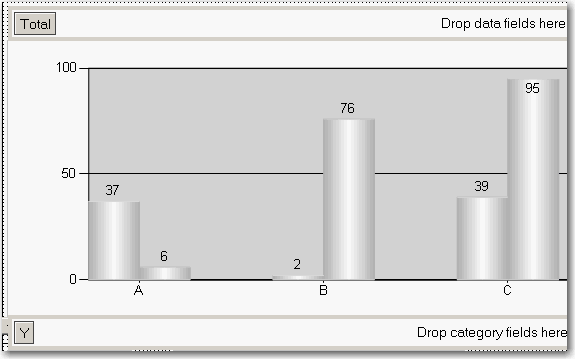
Figure: Build up the column chart in layout view - Now you need to set the last column to be a different color so it stands out. Right-click the chart and click Properties.
- Click the "Data" tab, click "Edit..." next to the "Values" box, then go to the "Appearance" tab and click "Series Style..." then the "Fill" tab.
- In the "Color" textbox, enter this expression, then OK all dialogs to return to the report:
=iif(Right(Fields!Y.Value, 2)=Month(Parameters!pEndDate.Value), "Blue", "Green")Users of the report service will find the data easier to understand and compare. However, in order for the report to be understandable, the data and chart must be clear and uncluttered.

Figure: Bad example - Just a chart - poor scaling for only 1 record 
Figure: Bad example - Just a chart - poorly scaling when many records The reason for this problem is that the 'size' property of the chart control doesn't support expressions like 'Count(Rows) or queried values like 'Fields!RowCount.Value', so the chart control cannot adjust its size according to the data.
The solution for this problem is to use an embedded chart within the table - this will create a dynamic chart list similar to the list shown below.
Figure: Size property of the chart control 
Figure: Good example - A table with chart To do this, you need to create a table in your report and add a chart into each of the rows.

Figure: Embedded chart in a table will generate dynamic chart list Note: When rendering a report to your browser or an email, Reporting Services generates a separate image for every single image in the report, even if they are identical. When you are using graphs, images or charts in your report, this can cause a large number of images to be generated. Always include a red warning at the top of any emailed reports so that users do not try and forward or reply to them. Use a warning like this:
Warning: Do not reply to or forward this report in an email - Outlook may slow down or even hang.
In Reporting Services 2005 you can use an expression to specify the scale of your charts. If you do not specify a maximum value for your y axis, the bar charts become inaccurate, as you can see in this figure.
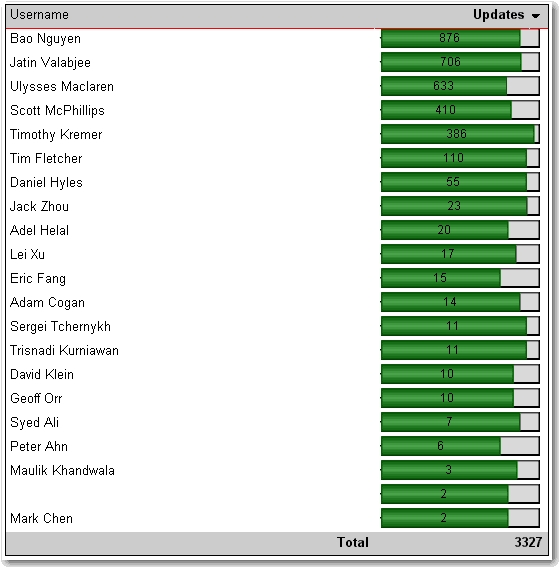
Figure: Bad example - With no scale value set, the charts do not display based on the correct scale Here's how to set the scale.
- In Layout view, add a new row to the bottom of the table
- At the bottom of the column with the chart, set the textbox value to =Max(Fields!MyTotal.Value), where "MyTotal" is the Data field you're using in the chart.
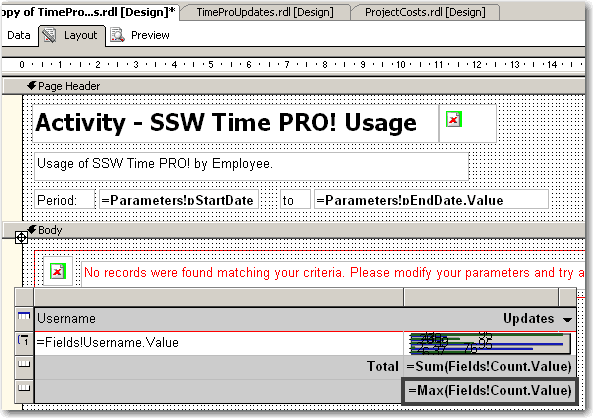
Figure: Add a new row to your table and set the max value - Set the textbox's Name property to MaxMyTotal (e.g. MaxCount)
- Set the new row's Visibility/Hidden property to true - you don't want to show it in the report
- Open the Chart properties and select the "Y Axis" tab
- Set the Maximum value to the value of the textbox, i.e. "=ReportItems!MaxMyTotal.Value"
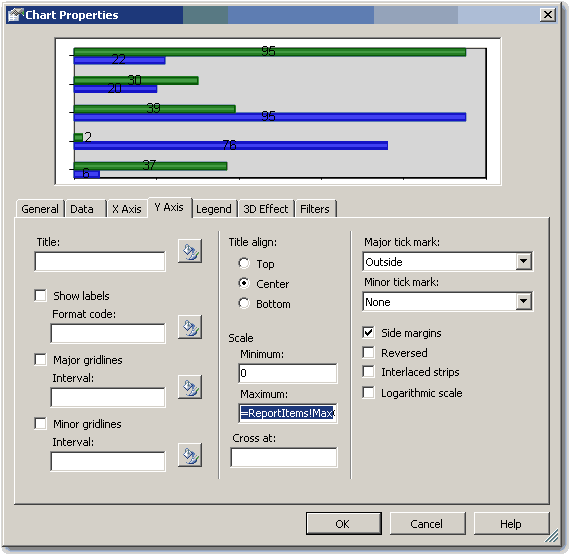
Figure: Set the maximum value to the value of the textbox - If you expect to have negative values in the chart (e.g. when comparing 2 values), set the Minimum to -1 multiplied by the max value, i.e. "=-1 * ReportItems!MaxMyTotal.Value". Otherwise set it to 0 (zero).
- If you expect to have negative values in the chart, select the chart value in the Data tab and click "Edit..." . Go to Appearance->Series Style->Fill and enter the following expression:
=iif(Fields!Change.Value > 0, "Green", "Red")Where "Change" is the name of your data field. This sets the color of the bar to green if it is positive, and red if it is negative
- Click OK and preview the report. The chart will now be using the maximum value across all the charts.

Figure: Good example - The scale is now correct This way is tedious and a "hack". We think that the scale should be automatically set with an option to customize it via an expression. See our suggestion about this on Microsoft SQL Reporting Services Suggestions.
Updated - fixed by Microsoft, see https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/reporting-services/report-design/set-a-minimum-or-maximum-on-a-gauge-report-builder-and-ssrs?view=sql-server-ver16&WT.mc_id=DP-MVP-33518
It is important to show previous and current data, as well as the changes between the two.
There will be cases in which the Change column has no meaning then you'd better to make this column invisible in your reports. In one of our reports we use an expression on Hidden property of this column to determine whether to show it based on the value of a parameter.
=iif(Parameters!ComparedExtractionID.Label = "N/A",true,false)Expression for Hidden property
When comparing two sets of data in a report (for example, sales this month compared to last), showing the change as a percentage is a bad idea.
For example, if you made 1 sale last month and 2 this month, you have had a 100% increase. If for another product you made 1000 sales last month and 2000 this month, that is also a 100% increase, but you've sold 1000 of that product compared to 1 of the other product.
For this reason, show the difference as an actual value, so you can compare all values easily. See the figures below for examples. To see how to create the negative/positive valued chart, see Do you use expressions to show the correct scale on charts?
Bad - Notice how the "change" column in the report doesn't accurately reflect the difference in downloads - 1 download last month and 2 downloads this month will yield a 100% increase - which looks impressive as a percentage but really isn't.

Figure: Bad example - The percentage change column in this Reporting Services product downloads report is misleading Good - This works better just showing the difference between the two values over the 2 months.
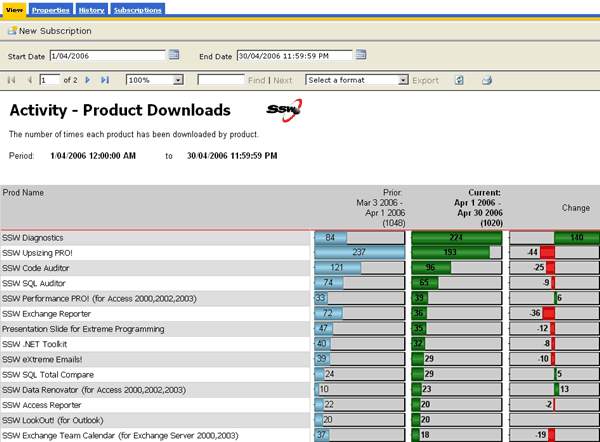
Figure: Good example - The column works better as just a difference between the current and previous download totals For readability, always use alternating row colors.
Use White and Gainsboro (a light shade of grey). Select the row, and enter this expression in the BackgroundColor property:
= iif(RowNumber(Nothing) Mod 2, "White", "Gainsboro")
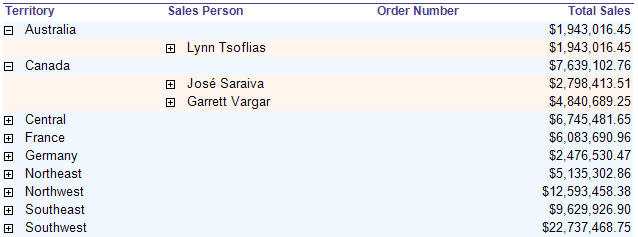
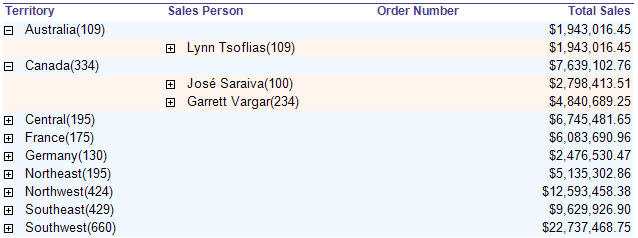
Figure: Good example - Alternating row colors greatly improve the readability of reports, and is very easy to do in Reporting Services A report with drill through like this should have the number in nodes like Outlook.
Here's how to add nodes count to the textbox with "collapsed(+)" in your report:
In the Expression property of the Textbox, add an expression to show nodes count. Use the following expression:
--Change the SQL ( or add a new DataSet ) SELECT a.TerritoryID, ( CONVERT ( varchar,a.TerritoryDescription ) + ' (' + CONVERT ( varchar, count ( c.TerritoryID ) ) + ')' ) AS Number, ... FROM Territories a INNER JOIN EmployeeTerritories b ON a.TerritoryID=b.TerritoryID, ... GROUP BY a.TerritoryID, a.TerritoryDescription,... --Expression to show nodes count = Fields!Number.ValueBad example - Get the Outlook Node Count look by changing the SQL.
--Expression to show nodes count = Fields!Name.Value + "(" + CStr ( CountRows( ) ) + ")"Use the CountRows() function to get the Outlook Node Count look
Note: The CountRows function is one of the several native functions provided by Reporting Services and returns the count of rows within a specified scope. If no scope is specified, it defaults to the innermost scope, which in our case resolves to the static group that defines the values in the data cells.
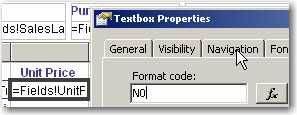
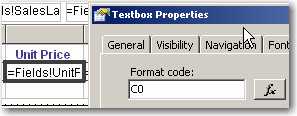
Having decimal places is generally not required when the numbers are there to show a general indication.
Only include decimal places on reports for accountants that will be used for reconcilations.
Here's how to remove decimal place in your report:
In the Expression property of the Textbox, add an expression to format currency values. Use the following expression:
--Expression to remove decimal place c0 = FormatCurrency( Sum(Fields!TotalDue.Value), 0)Note: The FormatCurrency function is one of several native functions provided by Reporting Services and returns an expression formatted as a currency value using a currency symbol according to the language setting on the textbox.
What is some managers don't want decimals and accountants do?
For some users (usually accountants) the number is critical to accurate reporting and reconciliation. In such cases, add a parameter to let the users choose.
This workaround should not be necessary. See the suggestion to Reporting Services ?Give users a runtime option to increase or decrease decimals places, so we don't need this workaround.
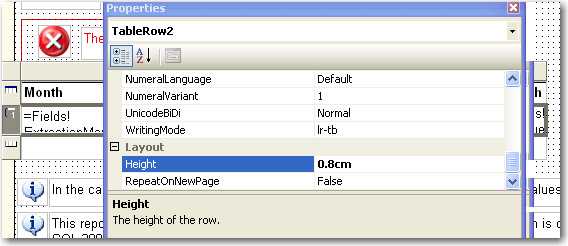
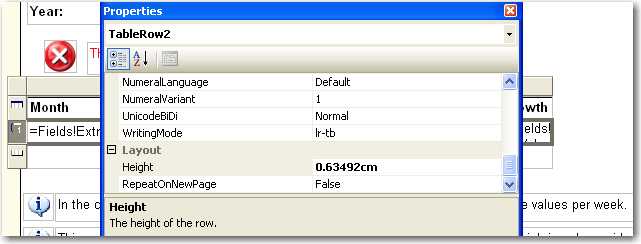
Figure: Good example - Add a parameter to set the decimal places format Same height of table row across all reports gives users consistent and professional impression.
We use the default height of table row (0.63492cm) as a standard to make sure all tables in our reports have consistent row height.
This rule also applies to height of Textbox in all reports.

Figure: Bad example - Bad Height 
Figure: Good example - Good Height We have a program called SSW Code Auditor to check for this rule.
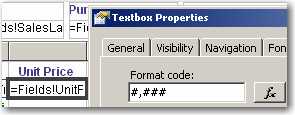
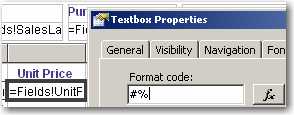
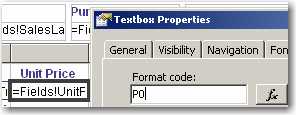
It looks better to display zero numbers as blank than to leave lots of '0' in a report.

Figure: Bad example - Bad zero number format 
Figure: Good example - Good zero number format It's easy to do with a simple format code '#,#'.

Figure: Format code It will give a professional look for your report to show time in a clear and consistant format.
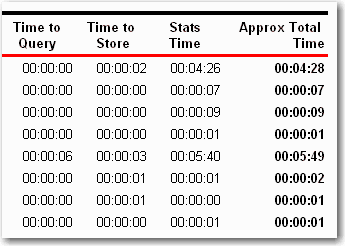
Figure: Bad example - Bad time format 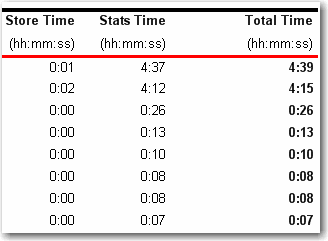
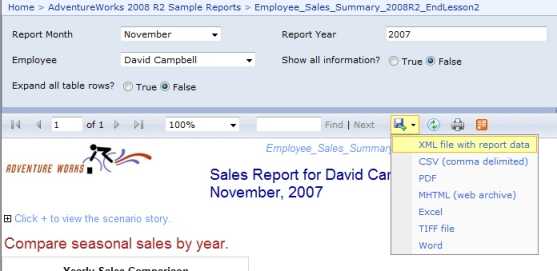
Figure: Good example - Clear time format It is much better to display all of the report parameters in report body, because it will be clear for users to know what they search not only in IE but also in exported file (PDF, Excel).
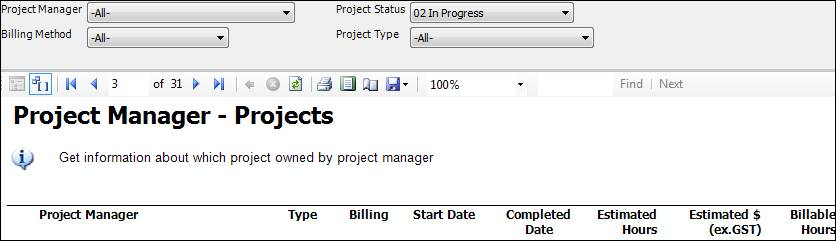
Figure: Bad example - Not displaying all report parameters 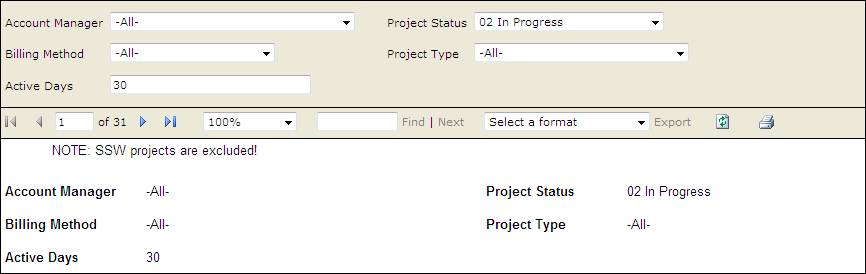
Figure: Good example - Displaying all report parameters Sometime you want your report to break at somewhere to separate different part of content into individual pages. A logical page break is what you need.
Logical page breaks are defined in the report definition by using the PageBreakAtStart and PageBreakAtEnd properties in various report elements, including group, rectangle, list, table, matrix, and chart.
Here is an example of how we add logical page breaks in a report to make each subreport start showing at right beginning in a new page.
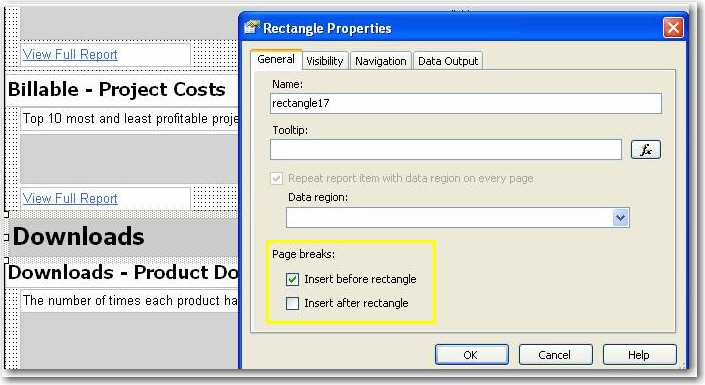
Figure: Insert a logical page break before a rectangle containing a subreport 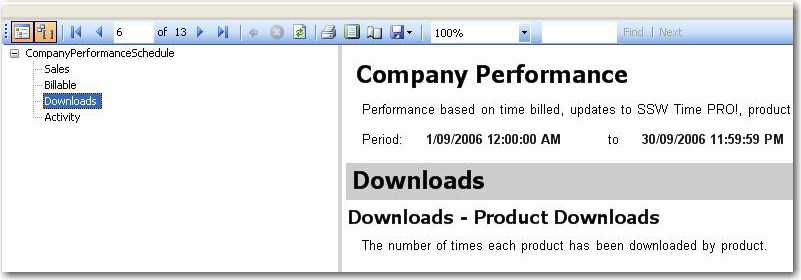
Figure: The subreport started in a new page By default charts in table grow with rows. This makes height of charts inconsistent and the report ugly.

Figure: Bad example - Inconsistent chart height Putting a rectangle in table cell and placing your chart in the rectangle fixes this problem.
Figure: Good example - Consistent chart height When a report has many columns and each column contains small amount of data, it is a good idea to use vertical text for the column headers.
By changing the WriteMode of a text box from:
lr-tb (left to right, top to bottom)To
tb-lr (top to bottom, left to right)...your text will become vertical, and you save lots of space.
Figure: Bad example - Not using vertical text for headings, when you have lots of thin columns 
Figure: OK example - Not using ticks and crosses Take it to the next level by using emojis in your report.

Figure: Good example - Use emojis to improve the quality of your report Emojis can add visual interest and make your report more engaging and easier to interpret at a glance.
Note: Microsoft have not given us the option of having the vertical text bottom to top. It would be easier to read. This suggestion has been added to Suggestions for Microsoft RS.
It's common that gray color means old, so we use gray for past data in reports.
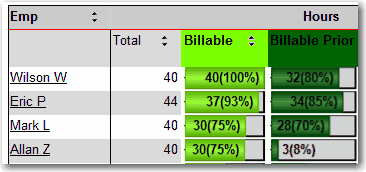
Figure: Bad example - Old data not in gray 
Figure: Good example - Old data in gray Most reports contain some sort of calculation - order totals, freight costs and so on. You have 3 options on how to display this in your report:
- Use an expression in the report (bad). Avoid doing this because your logic is scattered throughout the report, and also because this logic cannot be shared around reports or with your other web and windows applications.
- Call an assembly with the calculated logic (better). This is better than using a calculation expression because the logic can be shared over multiple reports, and it is easy to find as all the logic is inside the one .NET project. It is not the best solution because there is an extra level of complexity as you have to build, compile and reference the assembly containing the logic.
- Use a denormalised database field (best). This is the best way because not only is the calculated value accessible directly from the report's data set, but the value is already pre-calculated which can provide a performance improvement (compared to calculating the value each time the report runs).

Figure: Bad example - Avoid using expressions for calculated values 
Figure: Bad example - Avoid using external assemblies for calculated values - it adds an unnecessary level of complexity 
Figure: Good example - Use a denormalised database field for calculated values SQL Ranking functions are introduced since SQL 2005. With these handy functions, you can easily rank your data.
SQL Snippet SELECT Rank() Over(Order A.BillableTimeTotal Desc) As Rank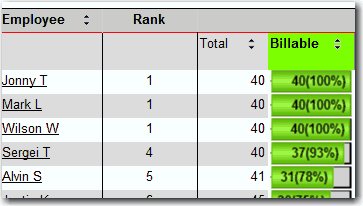
Figure: Good example - Rank by SQL Ranking functions When a user opens a report, they expect to see something. It is the developer's job to get the default values for parameters right. Default parameters allow the user to see what they expect... a report, and they also show users the expected format for parameters and make it easier to run validation tests to see if all the reports on your server are working correctly And of course you don't get it right by hard coding defaults.
The following report shows nothing, because the parameters are using meaningless default values (in this case, old dates for the year 2006)
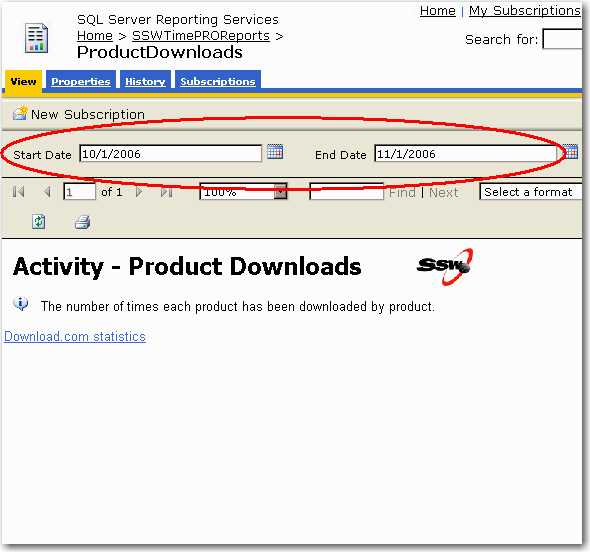
Figure: Bad example - Empty report caused by incorrect parameter default values (probably hard coded for when the developer wrote the report in 2006) 
Figure: Good example - This report shows initial data as the developer configure useful parameters (in this case default values for the entire month of October Note: in US date format) In SQL Reporting Services, parameters can be:
- hard coded
- an expression, or
- from a query
Hard coded values should never be used. Expressions may be good for some instances, but because it's not linked with your data, it may not be good enough.
--Expression to get the 1st day of the previous month (aka Start Date) DateSerial(iif( Month(DateTime.Now)=1, Year(DateTime.Now)-1, Year(DateTime.Now)), iif( Month(DateTime.Now)=1, 12, Month(DateTime.Now) - 1), 1) --Expression to get the 1st day of the current month (aka End Date) DateSerial(Year(DateTime.Now), Month(DateTime.Now),1) --Expression to get the 1st day of the next month DateSerial(iif( Month(DateTime.Now)=12, Year(DateTime.Now)+1, Year(DateTime.Now)), iif( Month(DateTime.Now)=12, 1, Month(DateTime.Now) + 1), 1)Bad example - Expressions to set the date range to the current month
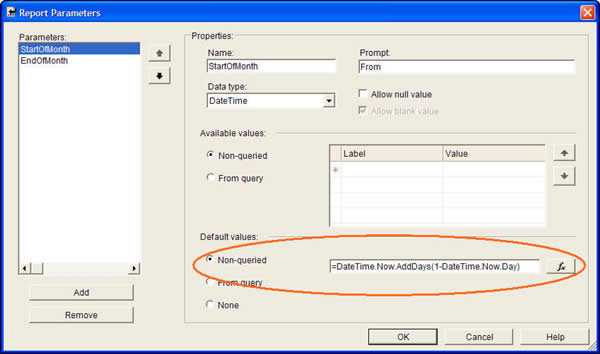
Figure: Bad example - Using an Expression to set the default values.(This will not be good enough if there is no data in the current month) The Solution:
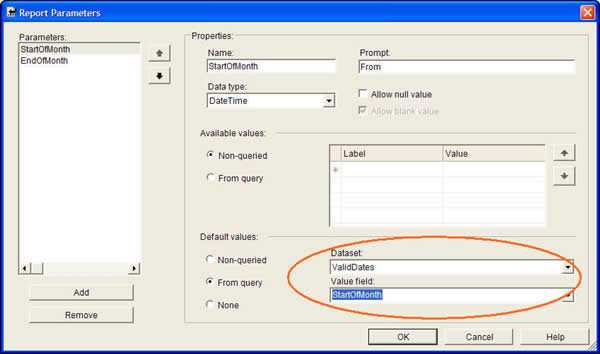
In order to give report parameters correct default values, you should always use query to generate these values from database. This will ensure your default values come from your data, so they won't fail to give some records.
**--Query to generate valid date from existing data** SELECT CONVERT( DATETIME, '1, ' + DATENAME(month, DATEADD(month, 1, MAX(OrderDate)))+ DATENAME(year, DATEADD(month, 1, MAX(OrderDate))) ) AS EndOfMonth, CONVERT( DATETIME, '1,'+ DATENAME(month, MAX(OrderDate))+ DATENAME(year, MAX(OrderDate)) ) AS StartOfMonth FROM OrdersGood example - Using a query to retrieve the last month of available data
The dataset 'ValidDates' looks similar to this:

Figure: Create a dataset to query the data and provide useful default parameter values for your report Use the DateTime data type for date parameters instead of using strings. There are 3 reasons to do this:
- Stop the bug "Cannot read the next data row for the data set" Although a hardcoded string will work, it will not work for all users regional date/time settings. E.g. a string data type parameter with a value of "26/01/2006" is correct for "dd/mm/yyyy", but it is wrong for "mm/dd/yyyy"
- When SQL Reporting Services is using the DateTime data type parameter, it will get the datetime value on the users setting (aka the Culture DateTime format).
- Your users also get the advantage of a date/time picker control, which automatically works out the correct regional date format. This solves the US/Australian date problem. (i.e. DD and MM are reversed).
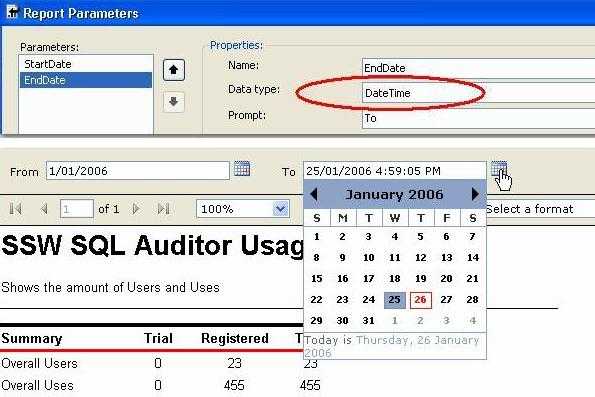
Figure: Good example - Use DateTime data type for the date parameter - you will not get internationalization bugs and it gives users a calendar control We have a program called SSW Code Auditor to check for this rule.
All display names referring to the same parameter should be consistent in everywhere of your reports. In addition, the parameter name and value should be in the same line if possible.
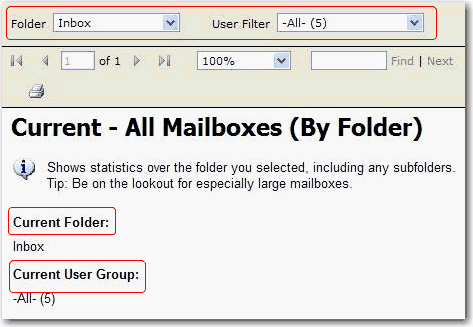
Figure: Bad example - Inconsistent parameter names 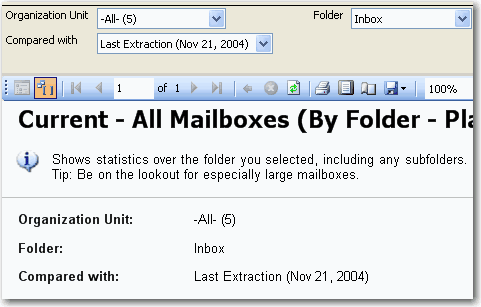
Figure: Good example - Consistent parameter names Note: If your data is not live, but based on ETL/SSIS Then each time log each import to a table Eg. Once a week. Then on the report parameters show this - so users know how old the data is.
When you have a large number of users all trying to access the same reports, the performance of your report server can suffer dramatically. Caching reports for a certain period of time can drastically reduce the load placed on the report server, leaving it ready to handle other requests.
When a report has caching enabled it only needs to be processed once within the expiry period. This means that when the first of your eager users hits that report, the report server will keep a copy until it expires, and will serve up this copy to any users that request the report within that period. This leaves the report server ready to process other reports quicker as it is not busy processing the popular reports over and over again.
For more information on setting up report caching please see the following KB article
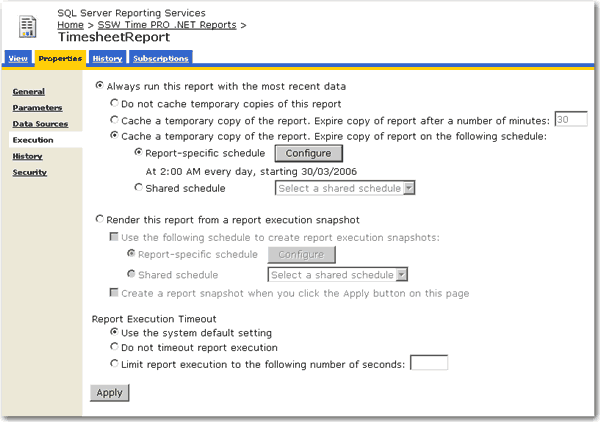
Figure: Enable caching for frequently used reports to improve performance A report should never take more than 30 seconds to run. Slow reports frustrate users, and also take valuable server performance away from the report server.
When dealing with slow reports, it is a good idea to setup scheduled snapshots. As an example, you would schedule a long running report to create a snapshot at night when the server is idle and not under a lot of stress. We recommend creating new snapshots every night so that the information displayed in the reports is never more than 24 hours old.
As an example:
Do create a snapshot for a sales summary Do not create a snapshot for an invoice report
For information on setting up scheduled snapshots see the following KB article

Figure: Create a scheduled snapshot of slow reports to improve performance Currency formatting is not universal - therefore, it's crucial to adapt the formatting to match regional conventions.
In Australia, one million is written this way: $1,000,000.00.But in Brazil, one million is written that way: $1.000.000,00.
So, in order to be culturally sensitive, try and use regional friendly formatting.
Developers too often change the 'Language' settings on reports in order to make it look ok for how they want to see it. Without realizing that they are now not supporting multiple cultures.
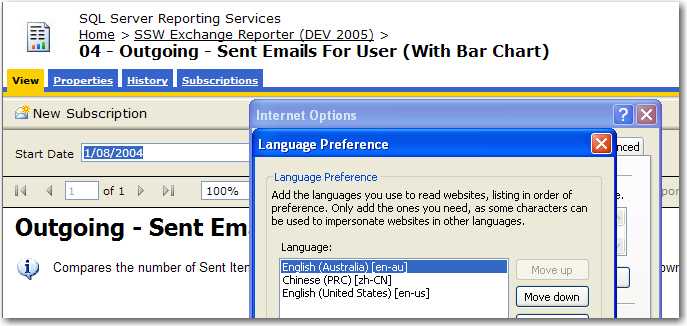
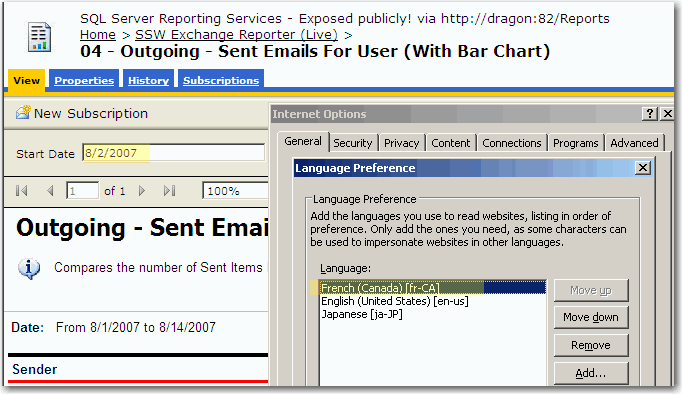
To do this, you need to set the 'Language' to "=User!Language". Then the report will recognize user client's culture settings, e.g. IE's languages settings.
Now you can specify this on either the culture sensitive controls or the whole report. Generally, is better specify this property on the whole report.
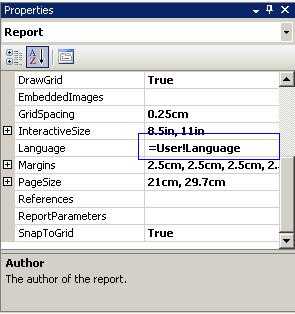
Figure: Good example - 'Language' setting is set to '=User!Language' to detect user's culture automatically 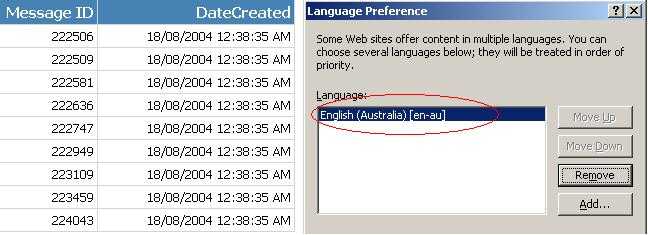
Figure: Good example - The data respects user's Language preference of IE in this case English (Australia) 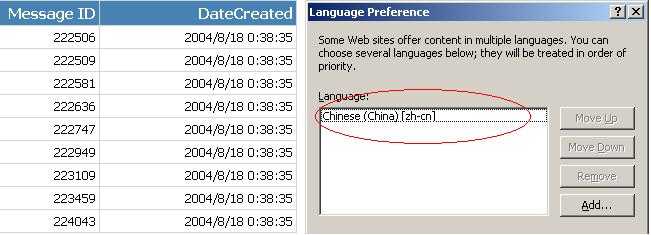
Figure: Good example - Likewise the data also respects user's Language preference of IE in this case Chinese (China) Warning: Adding the 'User' who printed the report, stops all data-driven subscriptions
When you try to add the 'User' your data-driven subscriptions fail with the following error:
'The '/GroupHealth' report has user profile dependencies and cannot be run unattended. (rsHasUserProfileDependencies)'.
The reason is the report doesn't know which language to choose. The workaround is to add a user function to fallback the error to a default language, like: "en-AU"
Public Function Language() Try Return Report.User!Language Catch Return "en-AU" End Try End FunctionGood example - Use above function to replace your reference to "Report.User!Language"/. It allows the subscription to work correctly
Currency formatting can vary significantly across cultures, and it's important to manage this effectively in your reports.
Although we can make the report support multiple cultures (as per Do you make sure your language follows the users regional settings?), we suggest you don't do this for currency fields. Instead:
- Have the Language set specifically to the culture you want. e.g. If you do a report for Australian Dollars, then it should be "English(Australia)"; if for Chinese Yuan, it should be "Chinese(People's Republic of China)". Because the format of currency should not change as per user's culture setting as $100 AUD <> 100 CNY !
- Have the currency column header set include the currency. Because $100 USD <> $100 AUD !
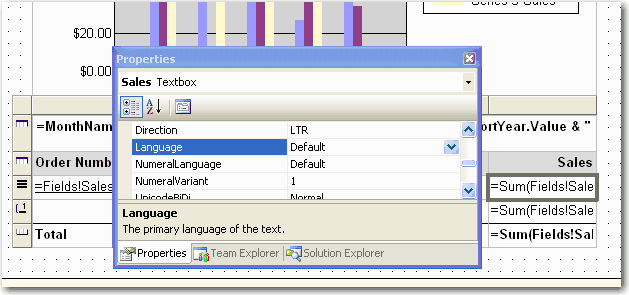
Figure: Bad example - Using default language for currency field 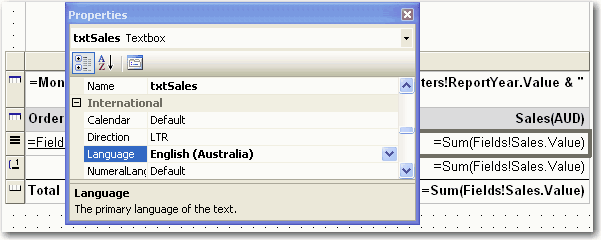
Figure: Good example - This currency field stores Australian Dollars and will always display it that way 
Figure: AUD currency 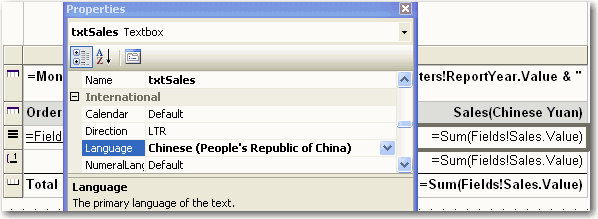
Figure: Good example - This currency field stores Chinese Yuan and will always display it that way 
Figure: Chinese Yuan currency If you don't want to get currency fields hard coded in reports, you can use an expression to read settings from your database.
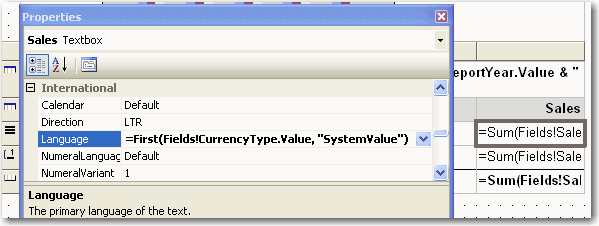
Figure: Good example - Using specified language as per value of column CurrencyType in table SystemValue Reporting Services does not have a build button, and thus, there is no way to verify that every single report is error free.Every Reporting Services installation should include this validator to check that all the reports are good.
Figure: SSW SQL Reporting Services Auditor SSW SQL Reporting Services Auditor is Web-Application that iterates through all the reports on a report server and shows whether they have rendered correctly or if any errors occurred.
The SSW SQL Reporting Services Auditor web application returns an XML dataset that can be consumed natively by SQL 2005 Reporting Services. The XML dataset can also be consumed by SQL 2000 Reporting Services; however, this requires you to write a custom Data Processing Extension as SQL 2000 Reporting Services does not natively support XML data sources.For more information read Microsoft's guide on Using an External Dataset with SQL 2000 Reporting Services.
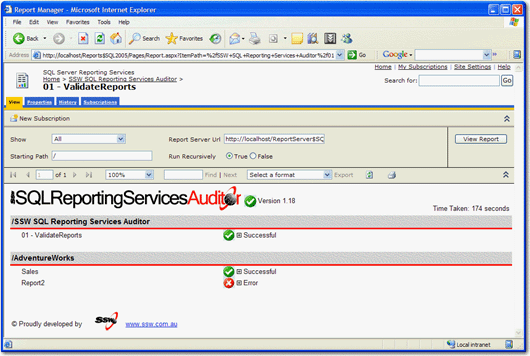
Figure: SSW SQL Reporting Services Auditor in Action! Download SSW SQL Reporting Services Auditor (Requires SQL Server 2005 Reporting Services).
To securely manage and provide public access to Reporting Services, configure separate ports for authenticated internal access and anonymous public access, following specific setup steps for both Windows Explorer and IIS Manager.
When going public with Reporting Services, you should have 2 ports:
- A public access port. This allows your public users to access their reports normally on a port which has been configured for anonymous users.
- An admin access port on your web site. This allows authenticated internal users to administer the report server via the Report Manager.
To set this up you need to perform the following:
In Windows Explorer:
- Create a Windows User account for the anonymous reporting services site to run as. e.g. IUSR_ReportViewer
- Open up the ReportingServices directory (C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL.3\Reporting Services)
- Duplicate the ReportServer and the ReportManager folders then rename postfix them with External e.g. ReportServerExternal and ReportManager_External
- Set the file access security on the new folders so that "Everyone" has full permissions.
- Edit the ReportServer_External/rsreportserver.config file. Update the URL node
<UrlRoot><http://xxxx:81/ReportServer></URlRoot> - the ReportManager_External/RSWebApplication.config file. Update the URL node
<ReportServerUrl>http://xxxx:81/ReportServer</ReportServerUrl>
In IIS Manager:
- Create another website on another port (i.e. port 81)
- Create Virtual Direcoties for ReportServer and Reports then point them to the new folders we just made. Make sure they are setup as applications.
- Change the Authentication of these 2 virtual directorys to use the user we have already created "USR_ReportViewer". Ensure that all other Authenticated access is unchecked.
- In the Reports Virtual Direcotry, make sure that it is running the same version of ASP.NET. Set the Applicaiton to execute Scripts and Executables. Add Home.aspx into the Default Documents.
- In the ReportServer Virtual Directory, make sure that it is running the same version of ASP.NET. Remove all the Application Mappings in the Application Confguration. Then add a wildcard mapping to the executable
C:\WINDOWS\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v2.0.50727\aspnet_isapi.dll
In SQL Management Studio
Add the user for these folders to have access in SQL.
In Reporting Services
- Go to http://localhost/reports
- Click Properties -> New Role Assignment
- Enter in IUSR_ReportViewer and click Browser then click OK
Note #1: The default website will be used for internal Admin (secure) use, and a website on a different port (in this example we use port 81) will be used for external anonymous access.
Note #2: Do these steps again every time you install a Reporting Services service pack
Once complete, you should now have authenticated access available on the standard port (80) and public access available on the new port (81).
Note: We think we should have the ability to choose how IIS authenticates clients - read this Reporting Services suggestion.

Figure: Create a separate virtual directory for admin access The process is a little simpler in SQL 2000:
In Windows Explorer
- Open up the ReportingServices directory (typically c:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL\Reporting Services)
- Make a copy of the ReportManager folder and call it ReportManagerPublicAccess
- Duplicate the file access security settings on ReportManager in ReportManagerPublicAccess
- Edit the RSWebApplication.config in the ReportManagerPublicAccessfolder to point to
http://server:81/ReportServer
In IIS Manager
- Configure the default website's ReportsServer virtual directory to give access to IUSR_ServerName (for public access)
- Export the Report and ReportServer virtual directory to an XML file
- Create another website on another port (i.e. port 81)
- Add the Report and ReportServer virtual directories using the XML files created in step 2
- Set the Reports virtual directory to point to the ReportsManagerSecure directory instead of just ReportsManager
- Set the directory security on the ReportServer on port 81 to use windows integrated security
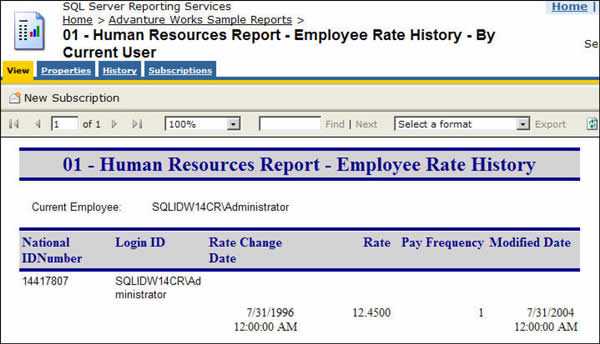
Payroll report should only show the records of the current user, Reporting Services support "Integrated Security" which you can use to identify the user who is running the report and only return relevant result for the current user.
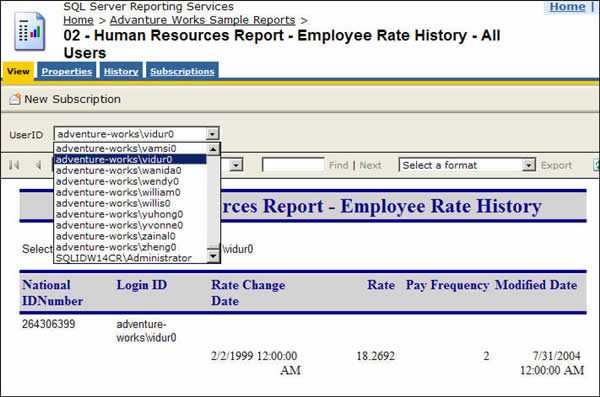
Figure: Bad example - Everyone can see others' rate changing history (maybe useful for administrative, but not for your employees) To generate such a report, you need to use the filter on the data table:
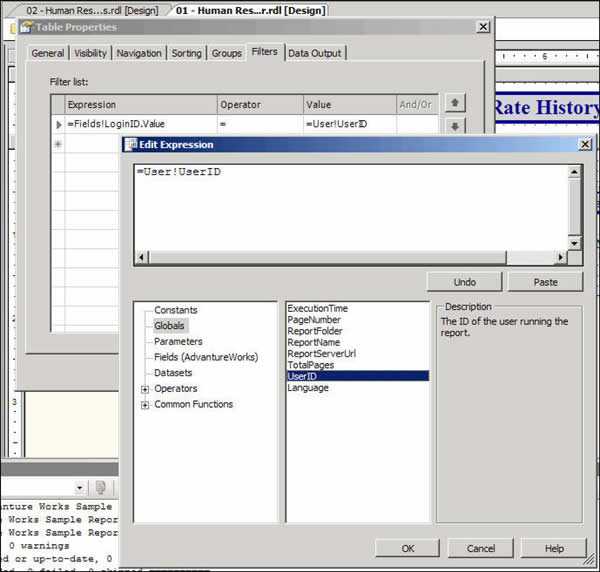
Figure: Specify the filters on your data table and select Globals->User!UserID Note: 'Edit Expression' dialog is only available on RS 2005, but the UserID global variable is available on RS 2000.
In subscription settings, @ExecutionTime should be removed from subject, because it ruins conversation threading in Outlook - You cannot sort them by subject.
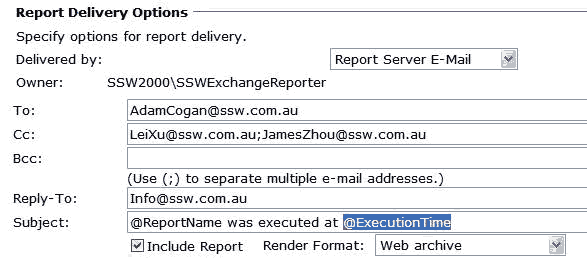
Figure: Bad example - Keep @ExecutionTime in subject So we always make subject of subscription exactly same as report name.
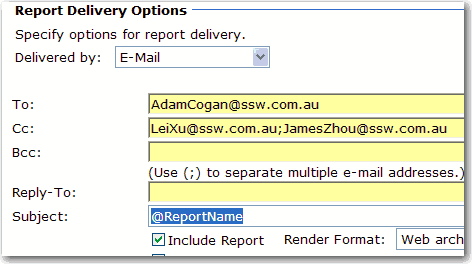
Figure: Good example - Subject same as report name You can get email list in ExtensionSettings, which is an XML column in Subscriptions table in database of reporting services. Subscriptions table has a FK with Catalog table, which contains report name and report path information. Then we can XQuery the ExtensionSettings to get TO and CC fields according to report name and report path.
See the following example. You need to fill report name and report path parameters(@mReportName and @mReportPath). Then this example will return the email dataset of the report's subscriptions.
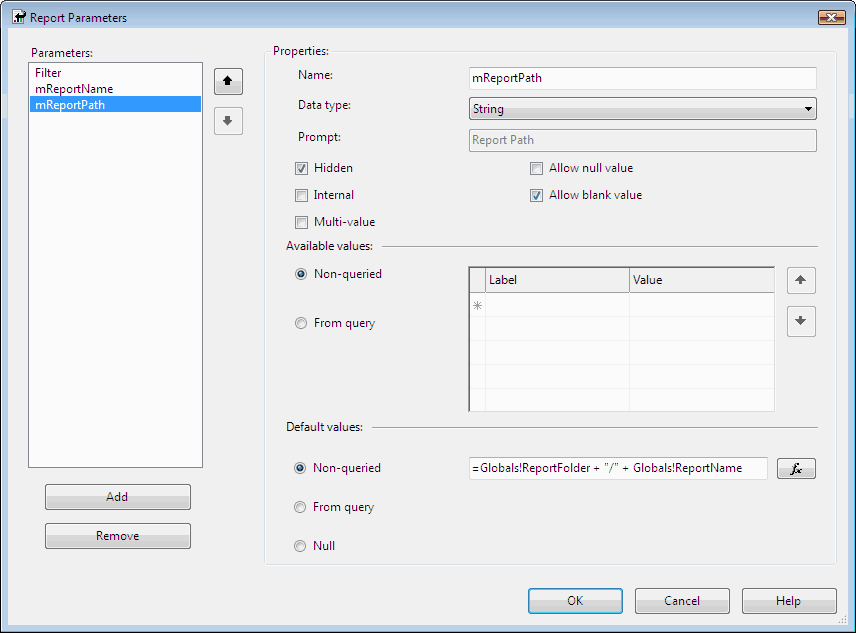
Figure: Report parameters 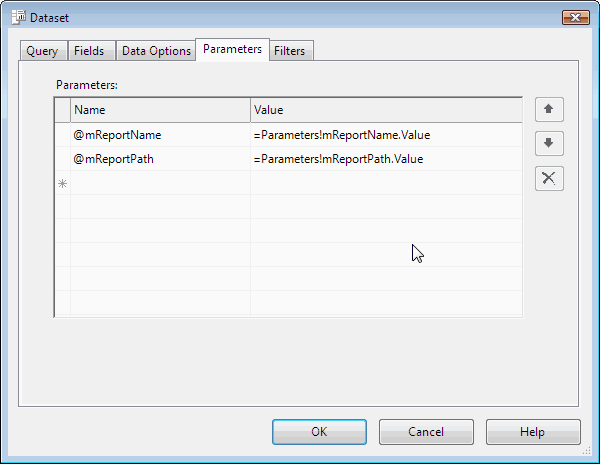
Figure: Transfer parameters to dataset DECLARE xmlCursor CURSOR FOR SELECT ExtensionSettings FROM SubScriptions, [Catalog] WHERE SubScriptions.Report_OID = [Catalog].ItemID AND [Catalog].Name = @mReportName AND [Catalog].Path = @mReportPath DECLARE @settingsXML AS XML DECLARE @toEmail AS XML DECLARE @ccEmail AS XML DECLARE @comment AS XML CREATE TABLE #subscrpt(toEmail XML, ccEmail XML, Comment XML) OPEN xmlCursor /* Perform the first fetch.*/ FETCH NEXT FROM xmlCursor INTO @settingsXML /* Check @@FETCH_STATUS to see if there are any more rows to fetch.*/ WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0 BEGIN SELECT @toEmail = @settingsXML .query('data(/ParameterValues/ParameterValue [Name = "TO"]/Value)') SELECT @ccEmail = @settingsXML .query('data(/ParameterValues/ParameterValue [Name = "CC"]/Value)') SELECT @comment = @settingsXML .query('data(/ParameterValues/ParameterValue [Name = "Comment"]/Value)') INSERT INTO #subscrpt VALUES (@toEmail,@ccEmail,@comment) /* This is executed as long as the previous fetch succeeds.*/ FETCH NEXT FROM xmlCursor INTO @settingsXML END SELECT toEmail, ccEmail, Comment FROM #subscrpt DROP TABLE #subscrpt CLOSE xmlCursor DEALLOCATE xmlCursorGood example - Get email list
Report owner is the person who looks after this report. It's a good way to put the owner on the report in order to get any response or suggestion on time.
There are four things you have to take care of.
- Please make sure you use a group (or a team) as the report owner rather than individual names. We do this to reduce maintenance work - whenever a person comes or leaves we do not need to modify the report.
- Make the report owner a hyperlink which links to the definition of the group (or the team).
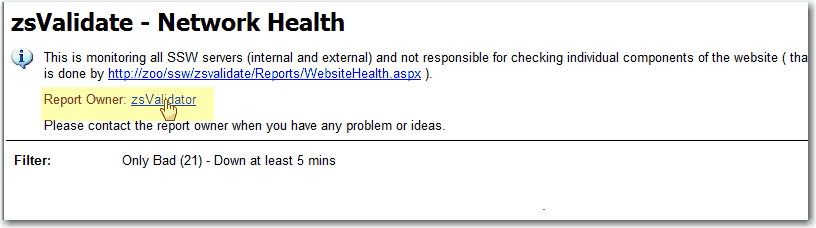
Figure: Good example - Show report owner in the report - When you cannot refer to a group, refer to the person Use the same idea for web pages, however in that case use the term "Page Owner"
- In CRM, the report can read from the CRM database since the report owner is stored by CRM against the report:

Figure: Good example - CRM - You already have a report owner so display this in your report Double line box makes reports look messy and inelegant, so it is better to use single line box.
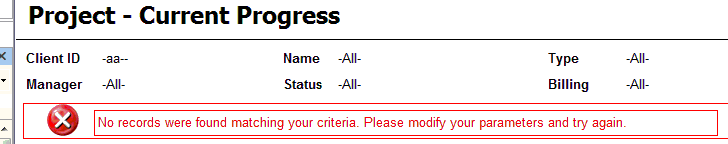
Figure: Bad example - Double line box makes the report above look messy 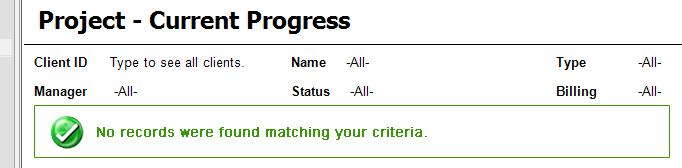
Figure: Good example - Single line box makes the report above look clean and elegant Using anonymous authentication is not recommended because of security reasons.
- Anonymous accounts (the IUSER*and IWAM* accounts) are managed by windows security system. We do not want to use these accounts because we have to manually configure our report server security settings.
- We do not want everyone on the Internet update or overwrite stuffs on the report server. Besides, anonymous authentication is no longer supported in RS 2008.
The best way to expose your report is to use ReportViewer and setup the credentials on it using ReportViewerCredentials.
Dim userName As String = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings("ReportViewer_UserName") Dim password As String = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings("ReportViewer_Password") Dim domain As String = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings("ReportViewer_UserDomain") reportViewer.ServerReport.ReportServerCredentials = New ReportViewerCredential(userName, password, domain) Dim paramList As List(Of ReportParameter) = New List(Of ReportParameter) paramList.Add(New ReportParameter("ClientContactID", mintClientContactID, False)) reportViewer.ServerReport.SetParameters(paramList)Warning: This is only supported for .NET Full Framework because of the ReportViewer component.
Reporting Service makes building, generating, managing and publishing report very easy, however sometime you want to refer to your report by URL from somewhere else. You will find that you can only link to the report default status, but not when you have changed the parameters. It should be as easy as using QueryString in ASP.NET application, but Microsoft didn't do that. See our Better Software Suggestions for Reporting Service.
A workaround for this is to use URL Access to build up a link by yourself then put it at the bottom of the report, so any time you want to refer to your current report status, you can just copy this link and put into your emails.
At SSW, we have "URL Access" at the bottom of reports for easy reference.
http://localhost/ReportServer/Pages/ReportViewer.aspx?%2fSSWTimePRO_CompanyPerformance%2f01+-+BillableTimeSummary&rs:Command=RenderBad example - Only refer to the default report URL, parameters on the report will be lost
http://localhost/ReportServer/Pages/ReportViewer.aspx?/SSWTimePRO_CompanyPerformance/01%20-%20BillableTimeSummary&rs:Command=Render&rs:ParameterLanguage=en-AU&pStartDate=1/06/2009&pEndDate=7/06/2009&pEmpID=ALZGood example - Refer to the report with all parameters ready
Note
rs:ParameterLanguage=en-AUin the query string, this is very important especially when you are passing culture sensitive data (DateTime) over URL. The server may not know your intended culture so you have to specify this together with the actual data in the URL.Refer to the following MSDN references for more details:
In reporting, total sales / revenue amount can be categorised as two types, which are include GST or exclude GST.
It is very important to have clear labelling to avoid the user guessing on whether it includes GST or exclude GST.
Leveraging live data feeds in Excel can transform static reports into dynamic, real-time insights, enhancing the analytical capabilities and streamlining report generation.
This is a great feature as it take advanatages of Excel 2010 PowerPivot together with Reporting Services 2008 R2 to allow end users to subscribe to live data from a report.
See what the experts said below:
"And that, by the way, makes it very useful, as it means that PowerPivot models can get data from Essbase and SAP BW (aka Netweaver BI) (via SSRS), which standard Analysis Services cannot do. But it also means that developers can write LINQ queries against reports and that whatever OData clients sprout up can get at that data as well. In general, it means that reports in SQL R2 support a RESTful interface." - Andrew Brust
"Using atomsvc feeds and loving it :) We've used this feature in our last 4-5 BI projects and the clients are all applauding this feature. It is a very nice way of surfacing information to users that want to use the information as a starting point for doing more analysis. It does indeed take a lot of the burden off the IT dept that previously had to build custom reports for everything." - Trond Brande
There are no specific rules for Reporting Service management beyond the general guidelines provided. However, you should adhere to the generic naming conventions used in other SQL Server contexts, such as avoiding plurals in folder names and using a "zs" prefix for system folders.
With the use of SharePoint 2010 Integration mode of Reporting, users can have the following advantages:
The users can easily deploy data sources, reports to sharePoint document libraries instead of Report Manager.The users can be much more self-sufficient with SharePoint.Very easy one step configuration of the add-in37 languages supported including bi-directional languages.Accessing Reporting in local mode when Access Services is enabled.Improved Report Preview experience with Report Builder 3.0 and edit sessions and deploy their reports to SharePoint document libraries, leveraging SharePoint for security.The users can take advantage of the new version of Report Builder that came with SQL Server 2008 R2 and deploy their reports to SharePoint document libraries, leveraging SharePoint for security.
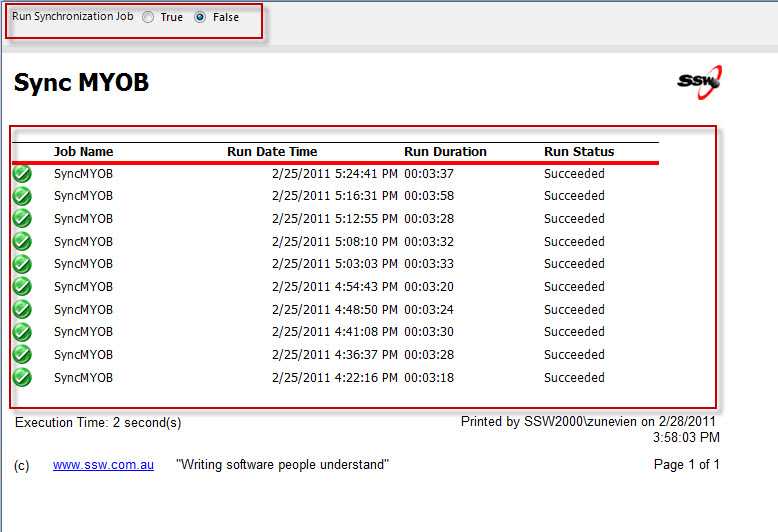
If you have a SQL database data source with data coming from an external source (i.e. MYOB), then you should create a report which allows user to manually refresh data.
Your report should have:
- A checkbox/radio button which allows user to trigger the refresh.
- A table display the history of previous refresh including start time, duration and status...